Blood Feeder Collection
"Blood Feeder: Exploring the Intricate World of Blood-Sucking Insects and Parasites" Delving into the microscopic realm
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
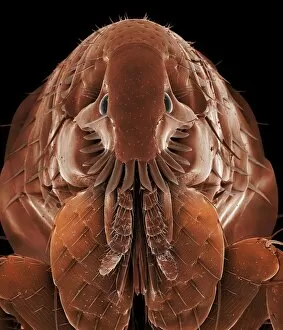
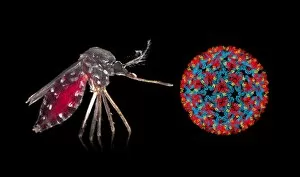
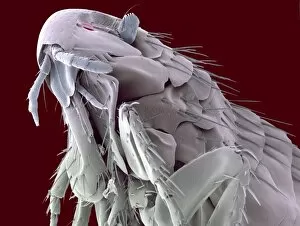
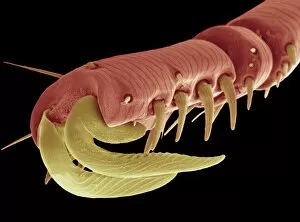
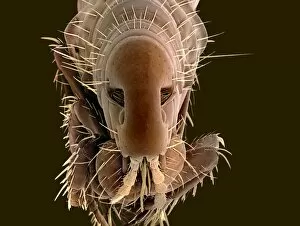
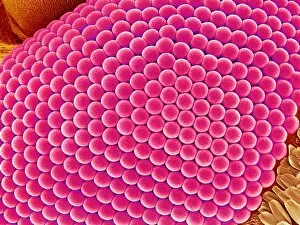
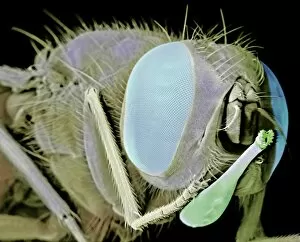
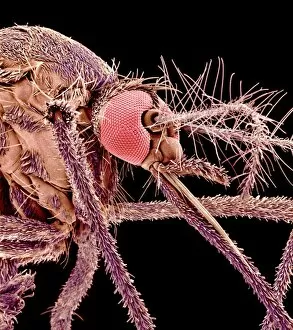
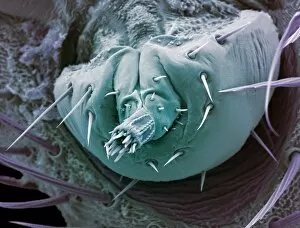
"Blood Feeder: Exploring the Intricate World of Blood-Sucking Insects and Parasites" Delving into the microscopic realm, we encounter the Sheep tick under a scanning electron microscope (SEM), revealing its intricate anatomy. The notorious Anopheles mosquito takes center stage, known for its role in transmitting deadly diseases like malaria to millions worldwide. Zooming in further, we witness the fascinating mouthparts of midges captured by SEM, showcasing their unique adaptations for blood-feeding. A closer look at a Cat flea's head through SEM C014/4842 reveals astonishing details about this tiny creature's feeding mechanisms. The Aedes mosquito emerges as a carrier of not only blood but also the Chikungunya virus, shedding light on the dangerous consequences of their bites. Behold an engorged Ixodes tick, swollen with blood after feasting on its host - a reminder of these parasites' ability to cause harm and transmit diseases such as Lyme disease. Multiple images showcase engorged Ixodes ticks once again, emphasizing their insatiable thirst for blood and highlighting their potential impact on human health. Lastly, we encounter the Asian tiger mosquito - an invasive species that has rapidly spread across continents due to its aggressive biting behavior and capability to transmit various diseases including dengue fever and Zika virus. In this captivating journey through magnified imagery, "Blood Feeder" sheds light on nature's relentless pursuit for sustenance while reminding us of our ongoing battle against these formidable creatures that rely on our life force to survive.