Detector Collection (page 2)
Caption: Unveiling the Secrets of the Universe: Exploring with Detectors From unraveling the mysteries of particle physics to ensuring safety in hazardous environments
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
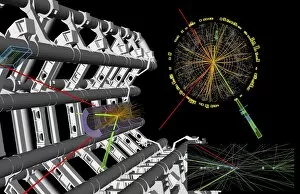
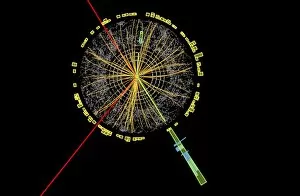
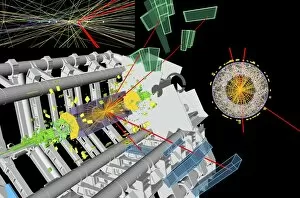
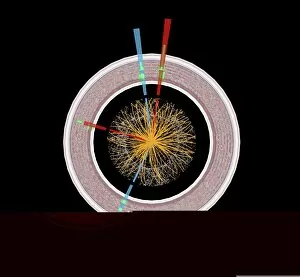
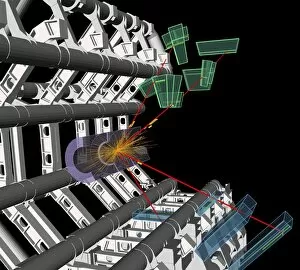
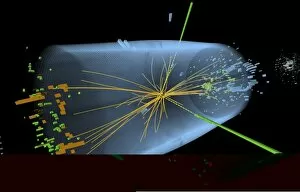
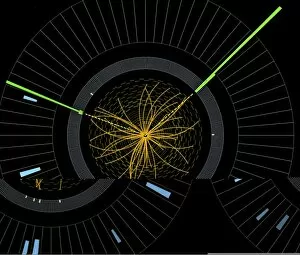
Caption: Unveiling the Secrets of the Universe: Exploring with Detectors From unraveling the mysteries of particle physics to ensuring safety in hazardous environments, detectors have played a pivotal role in various fields throughout history. In 2012, scientists at CERN's ATLAS detector (C013/6892) made a groundbreaking discovery by capturing the elusive Higgs boson event, shedding light on the fundamental building blocks of our universe. Just like miners relying on canaries to detect dangerous gases deep underground, detectors have been crucial for human survival. During World War II's Normandy Landings on June 6th, 1944, these devices helped soldiers navigate treacherous territories and identify hidden threats. Intricate simulations of Higgs boson production continue to push scientific boundaries. The CMS detector at CERN enables researchers to delve deeper into understanding this enigmatic particle and its role in shaping our universe. Computer artwork showcasing the ATLAS detector at CERN highlights how technology has advanced over time. This cutting-edge device aids physicists in their relentless pursuit of knowledge about particles and their interactions. Particle physics research owes much credit to detectors such as Fermilab's CDF particle detector. These instruments allow scientists to observe and analyze subatomic particles with unparalleled precision, leading us closer to unlocking nature's secrets, and are not limited solely to scientific endeavors; they also find applications beyond academia. Dating back as early as 1923, lie detectors have sought truth by measuring physiological responses during questioning sessions. The Harley-Scope Mine-Detector designed by William Heath Robinson exemplifies how inventors continuously innovate detection technologies for specific purposes. By saving countless lives during times of conflict or danger, these devices prove invaluable assets across diverse domains. As we venture further into uncharted territories within science and society alike, it is clear that detectors will remain indispensable tools for exploration and security alike – forever guiding us towards new frontiers of knowledge.