False Coloured Collection (page 4)
"Revealing the Unseen: Exploring the World Through False Colors" Step back in time to medieval alchemy
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
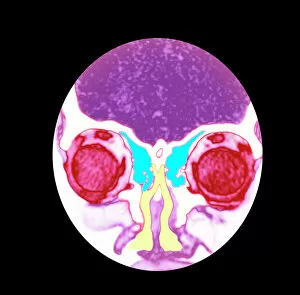
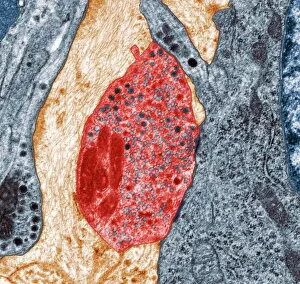
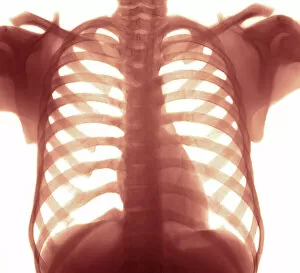
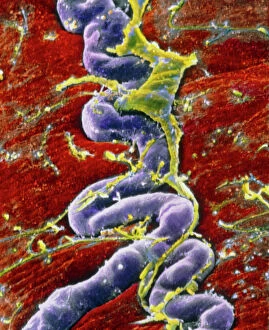
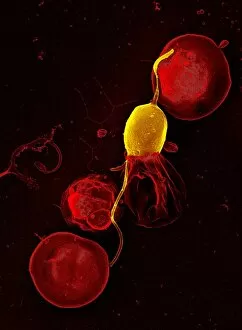
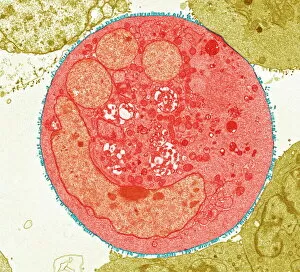
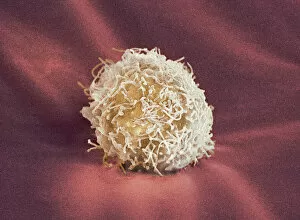
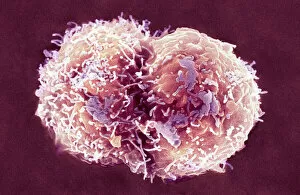
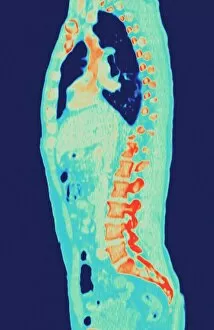
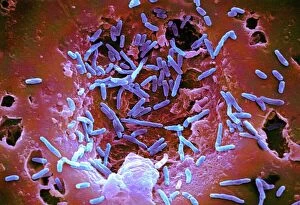
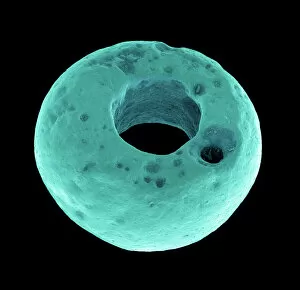
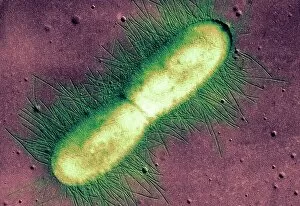
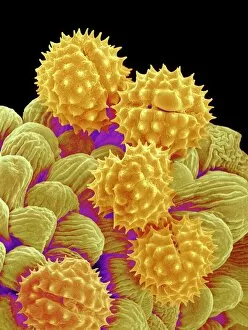
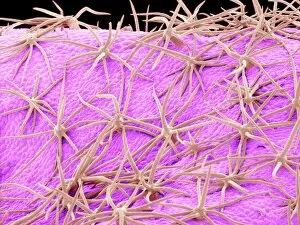
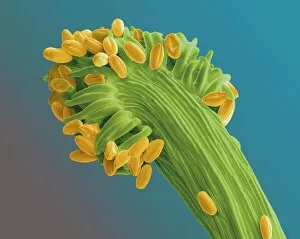
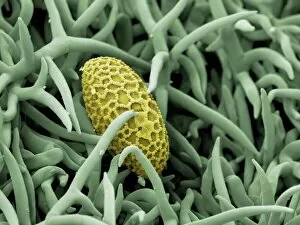
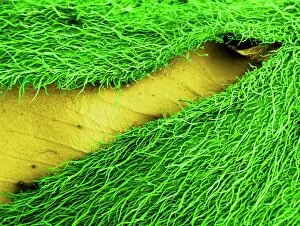
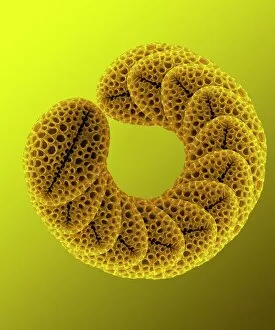
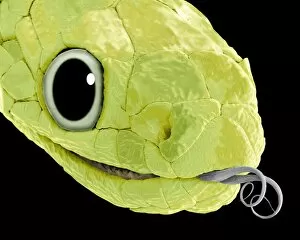
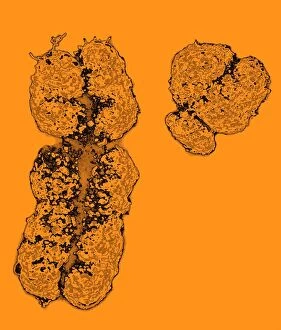
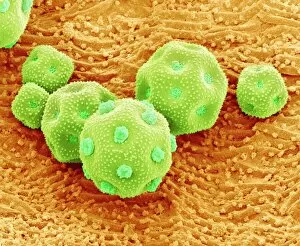
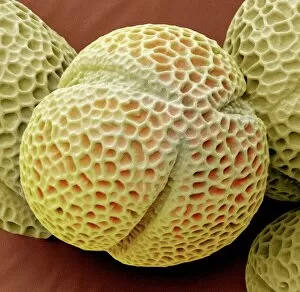
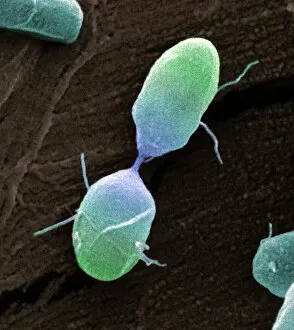
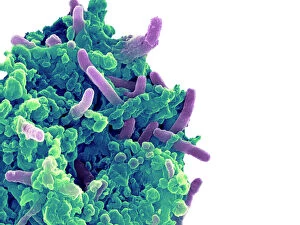
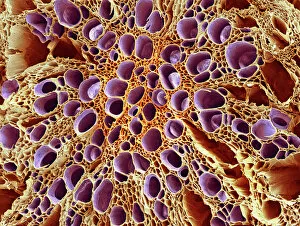
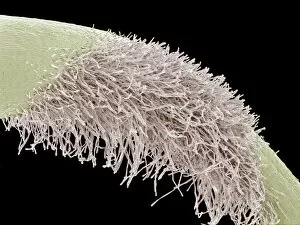
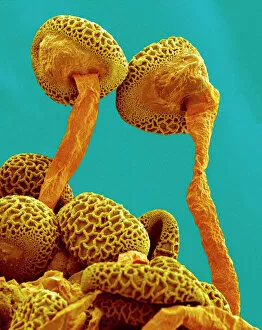
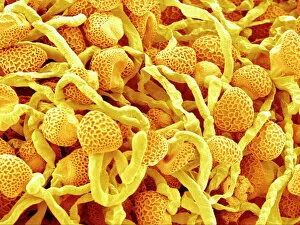
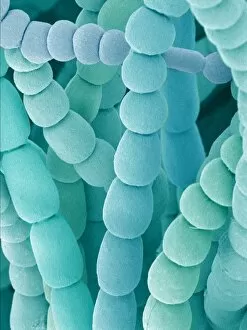
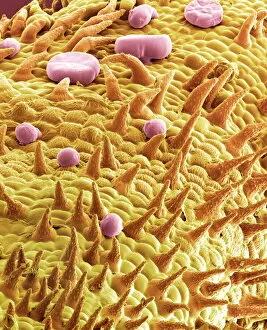
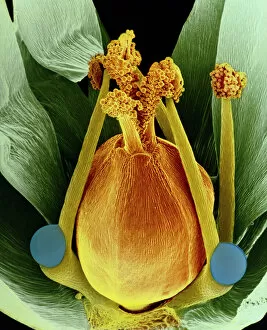
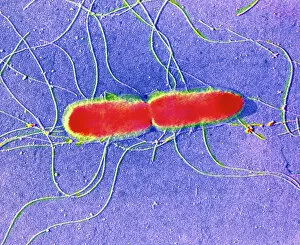
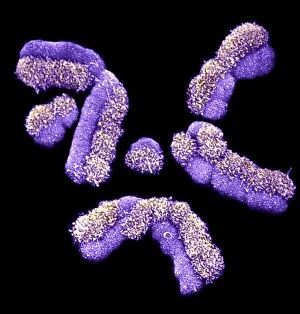
"Revealing the Unseen: Exploring the World Through False Colors" Step back in time to medieval alchemy, where a peculiar contraption known as the "Medieval urine wheel" was used to extract hidden secrets from bodily fluids. Fast forward to modern times and witness how science has evolved, unveiling breathtaking wonders like the Orion Nebula. Delve into the microscopic realm, where particle tracks paint a mesmerizing picture of subatomic interactions. Journey across Martian landscapes through the eyes of Spirit rover images, capturing otherworldly vistas that ignite our imagination. Peering into our own genetic blueprint, false colors bring clarity to X and Y chromosomes, unraveling mysteries within our very cells. A horse's skull takes on an ethereal glow as we explore its intricate structure using advanced imaging techniques. Witness synapse nerve junctions come alive with vibrant hues under a transmission electron microscope (TEM), revealing connections that shape our thoughts and actions. A person holding a camera becomes an enigma when captured through X-ray technology – their inner world exposed for all to see. Marvel at tardigrades' resilience as they navigate their microscopic universe under scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Calcareous phytoplankton dance with color in intricate patterns while nerve cells reveal their complexity in stunning detail. Travel back in time to 19th-century Cornwall and discover the harsh reality of tin mining brought vividly to life through false colors – reminding us of humanity's enduring spirit even amidst adversity. In this captivating journey through various realms – from ancient alchemy to distant galaxies, minuscule particles to majestic landscapes – false colors unlock hidden dimensions beyond what meets the eye, inviting us all into a world brimming with wonder and discovery.