Haematology Collection (#8)
Haematology, the captivating study of blood cells and their intricate functions, unveils a world unseen to the naked eye
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
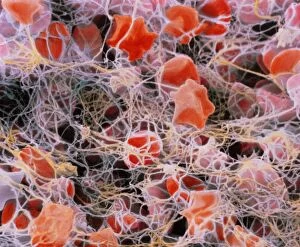
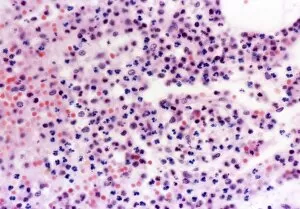
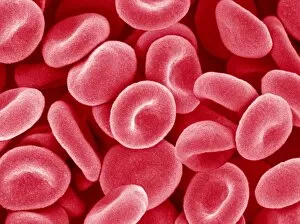
Haematology, the captivating study of blood cells and their intricate functions, unveils a world unseen to the naked eye. Through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), we delve into this mesmerizing realm where red and white blood cells take center stage. Witnessing these tiny heroes in action is truly awe-inspiring. The blood coagulation cascade, an essential process for wound healing, comes alive through artwork C016 / 9873. Each step meticulously depicted, showcasing the complexity behind clot formation. Meanwhile, SEM reveals the delicate beauty of red blood cells as they flow gracefully through our veins. Dohle bodies in a blood cell micrograph offer a glimpse into abnormalities that can occur within these vital components of life itself. Their presence hints at underlying health conditions that require further investigation. Acute promyelocytic leukaemia's impact becomes evident when examining its micrograph closely. The distorted appearance of affected cells serves as a stark reminder of the challenges faced by those battling this disease. Intriguingly, even on plaster surfaces under SEM scrutiny, we uncover unexpected encounters with blood clots - reminders that our body's defense mechanisms are always at work to protect us from harm. Computer artwork brings forth vibrant depictions of red blood cells dancing harmoniously together; their collective effort ensuring oxygen reaches every corner of our being. A testament to nature's remarkable design and efficiency. And let us not forget about stem cells – versatile powerhouses capable of transforming into various specialized cell types. SEM provides an up-close look at these extraordinary entities that hold immense potential for regenerative medicine and groundbreaking therapies. Finally, an enchanting connection between red blood cells and the heart emerges before our eyes – symbolizing life's unbreakable bond between circulation and vitality. Haematology unravels secrets hidden within each drop coursing through our veins - reminding us how intricately woven science is with human existence itself.