Hominoid Collection (#4)
"Hominoid: Unraveling the Evolutionary Tapestry" Delve into the fascinating world of hominoids
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
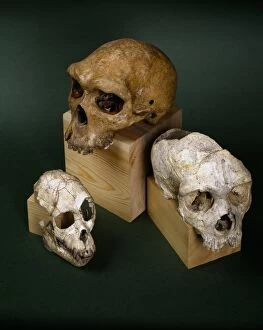
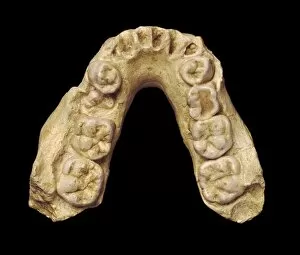
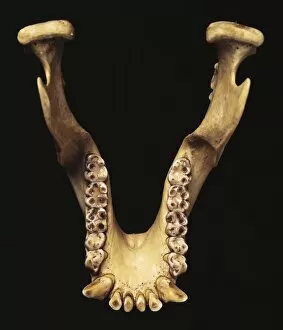
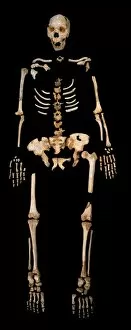
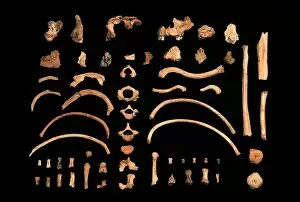
"Hominoid: Unraveling the Evolutionary Tapestry" Delve into the fascinating world of hominoids, a diverse group of primates that includes humans and their closest relatives. From the intricate sensory homunculus mapping our perception to the remarkable Australopithecus afarensis (AL 288-1), affectionately known as Lucy, these creatures hold secrets to our own origins. The study of hominid crania provides invaluable insights into our ancestors' physical characteristics and evolutionary journey. The iconic Australopithecus afarensis (AL 288-1) skull, famously named Lucy after its discovery in Ethiopia, offers a glimpse into an ancient species that walked upright millions of years ago. As we explore further, we encounter the motor homunculus – a representation of how different areas of our brain control specific body movements. Witness Homo neanderthalensis in action at Swanscombe, UK; imagine their strength and resilience as they roamed Europe thousands of years ago. Travel back even earlier with Proconsul africanus - an early ape-like ancestor believed to have lived around 23 million years ago. These reconstructions allow us to visualize how this creature might have looked like during its time on Earth. Continuing along this chronological path brings us face-to-face with Australopithecus afarensis once again. This species played a crucial role in human evolution by exhibiting bipedal locomotion and providing evidence for early tool use. Step forward in time to witness Homo heidelbergensis in action - an archaic human species that inhabited Africa nearly half a million years ago. Observe their resourcefulness and adaptability as they thrived across various environments. Not limited solely to humans, we also encounter Guy - a western lowland gorilla who lived from 1946 until 1978.