Immune System Collection (#28)
"The Immune System: A Complex Network of Defenders" Our a remarkable defense mechanism that safeguards our body against harmful invaders
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
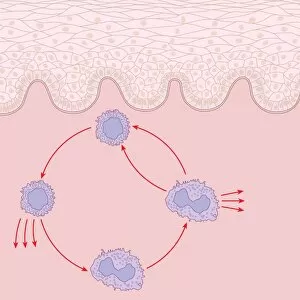
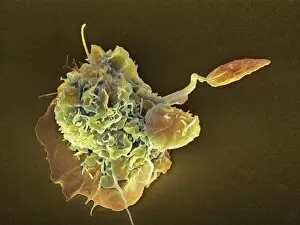
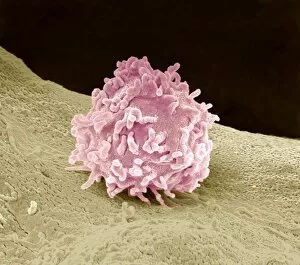
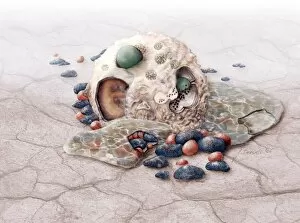
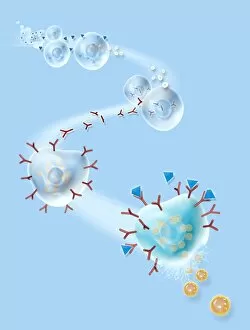
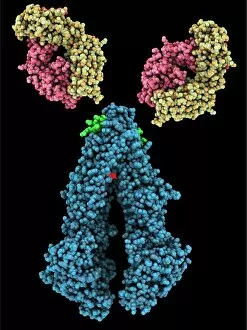
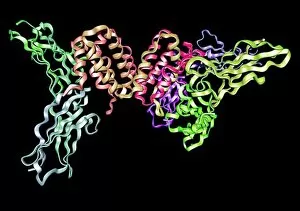
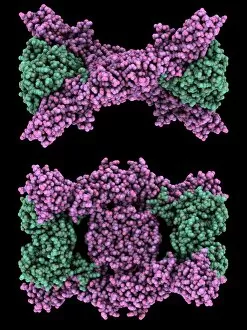
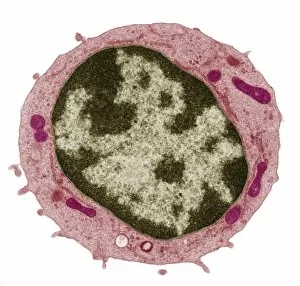
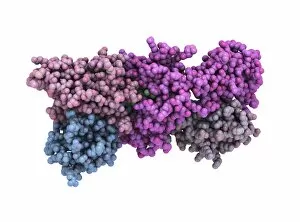
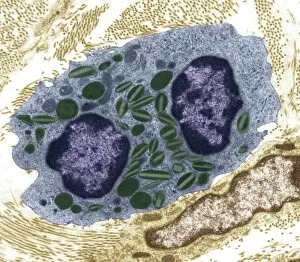
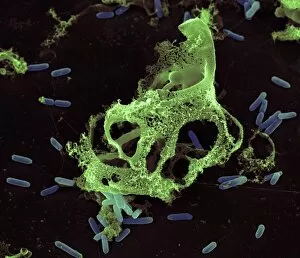
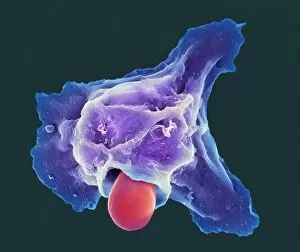
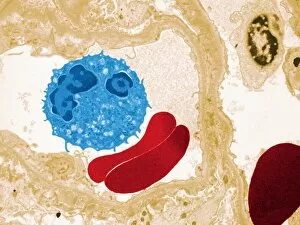
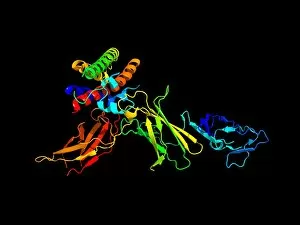
"The Immune System: A Complex Network of Defenders" Our a remarkable defense mechanism that safeguards our body against harmful invaders. At the forefront of this battle are T lymphocytes, specialized white blood cells capable of recognizing and destroying cancer cells. SEM C001 / 1679 reveals the intricate interaction between these vigilant warriors and malignant intruders. Another crucial component in our immune arsenal is the Immunoglobulin G antibody molecule, as depicted in F007 / 9894. These powerful molecules neutralize pathogens by binding to them, preventing their harmful effects on our body. Neutrophils, captured in action through SEM C018 / 8596, showcase their ability to engulf dangerous bacteria like MRSA. These fearless soldiers patrol our bloodstream, eliminating potential threats with precision and efficiency. Dendritic cells play a pivotal role in orchestrating immune responses. In an artistic representation, we see these sentinel-like cells capturing antigens and presenting them to other immune cells for recognition (artwork). The TEM image of a human white blood cell bearing HLA antigen highlights its significance in identifying foreign substances and triggering appropriate immune responses. Blood cells form the backbone of our immunity; they transport oxygen and vital nutrients while also serving as defenders against invading pathogens. Antibodies take center stage once again in captivating artwork depicting their diverse shapes and functions. They act as molecular weapons targeting specific antigens with incredible accuracy. Cortisol crystals under light micrograph remind us that stress can impact our immune system's performance. Managing stress levels becomes crucial for maintaining optimal immunity. Micrograph evidence showcases Dohle bodies within blood cells—an indicator of infection or inflammation—a reminder that vigilance is key to combating potential health threats effectively. An illustration portrays how vaccination triggers an orchestrated response involving microbes, antigens, antibodies, plasma cells (TEM), ultimately fortifying our defenses against future infections. Understanding the complexity and resilience of our immune system is essential.