Lymphocyte Collection (#3)
Lymphocytes: The Mighty Defenders of our Immune System Blood cells play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health, and among them
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
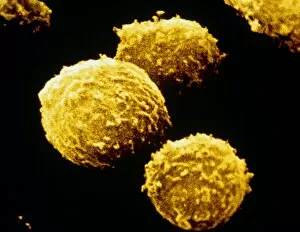
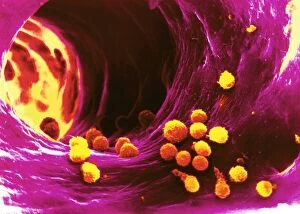
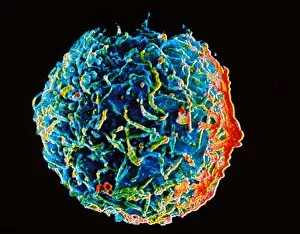
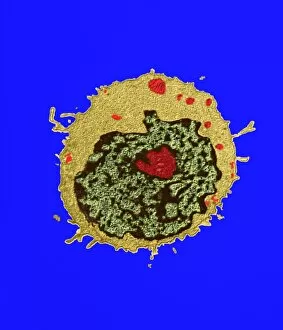
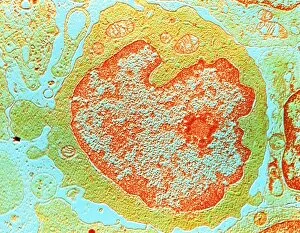
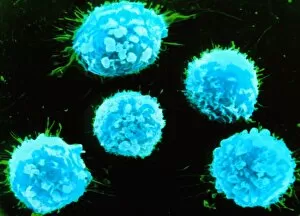
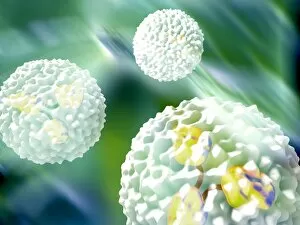
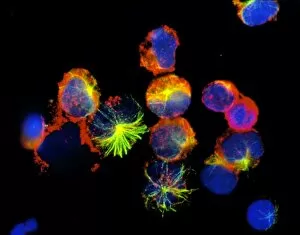
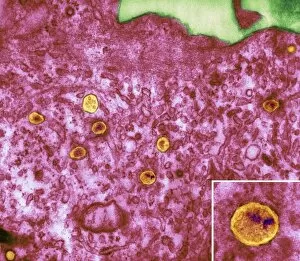
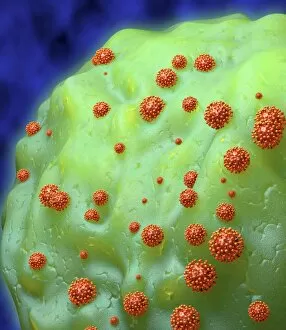
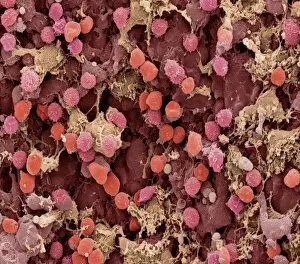
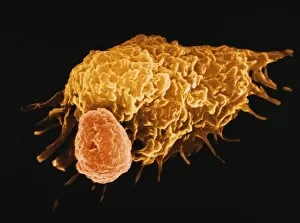
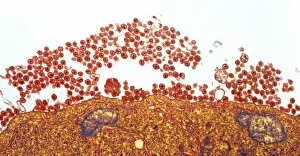
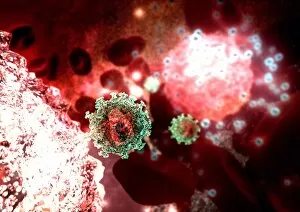
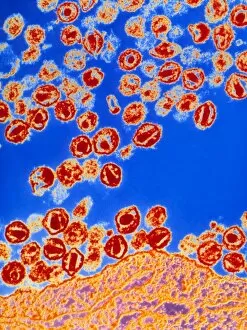
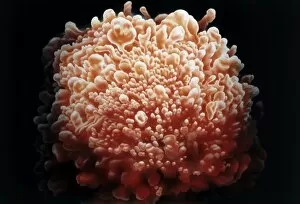
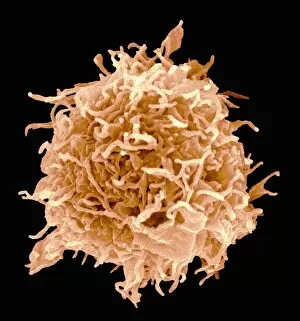
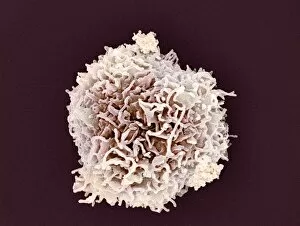
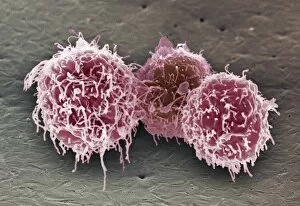
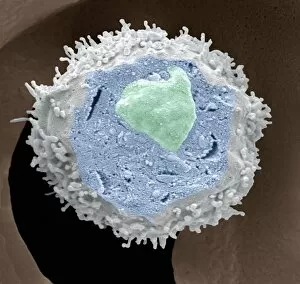
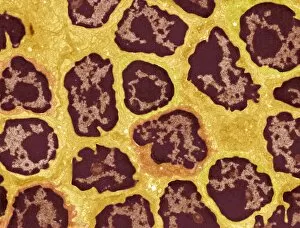
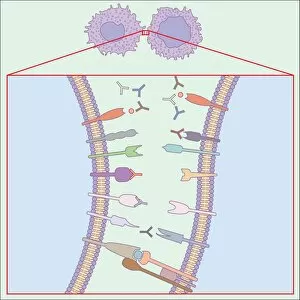
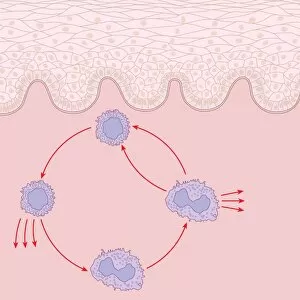
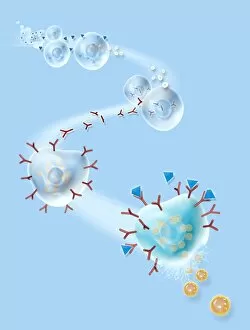
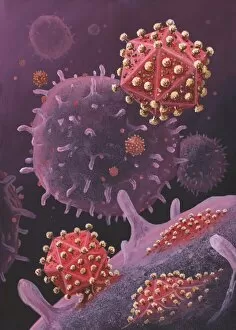
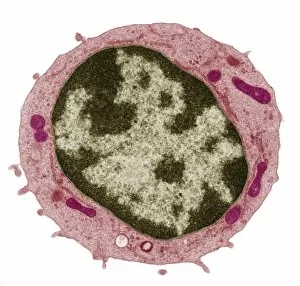
Lymphocytes: The Mighty Defenders of our Immune System Blood cells play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health, and among them, lymphocytes stand out as the true warriors. In this captivating journey through microscopic wonders, we explore the incredible world of these white blood cells. Through a colored scanning electron microscope (SEM), we witness the beauty of a lymphocyte up close. Its intricate structure reveals its readiness to combat any threat that may invade our body. Another SEM image showcases lymphocytes fearlessly attacking cancer cells, highlighting their vital role in fighting against this deadly disease. Moving deeper into the immune system's realm, we encounter plasma cells under a transmission electron microscope (TEM). These specialized lymphocytes produce antibodies that neutralize harmful pathogens and protect us from infections. An artistic representation captures the essence of these remarkable white blood cells. Their elegance is portrayed through delicate brushstrokes, reminding us of their tireless dedication to safeguarding our well-being. However, not all battles are won easily. A TEM image unveils HIV particles infecting human H9 T-cells – an unfortunate sight that reminds us of the ongoing fight against AIDS and emphasizes how crucial it is to support research for finding effective treatments. In another microscopic view lies a leukemia cell - a reminder that sometimes even our own defense mechanisms can go awry. This glimpse serves as motivation for scientists striving to understand and develop therapies for such diseases. Collaboration between different immune system components is key; thus, we observe macrophages working alongside lymphocytes in yet another TEM image. Together they form an unbreakable shield against invading pathogens or abnormal cellular growths. The battle against HIV continues with an astonishing TEM capture showcasing viruses budding from T-cells affected by AIDS—a stark reminder of how vital it is to raise awareness about prevention methods and provide support for those living with this devastating condition. Even within hair follicles lies evidence activity, as seen through a SEM image.