Metabolism Collection (#5)
"Unveiling the Mysteries of Metabolism
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
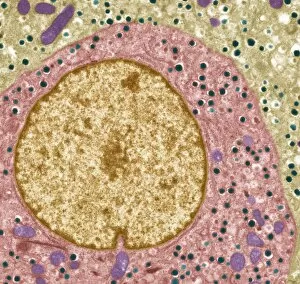
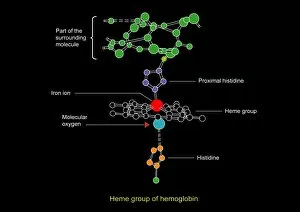
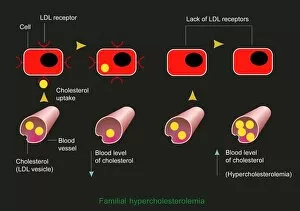
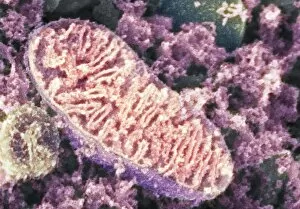
"Unveiling the Mysteries of Metabolism: Exploring the Powerhouses Within" Step into the microscopic world with TEM images revealing the intricate structure of mitochondria, the cellular powerhouses responsible for metabolism. Discover Theodor Schwann, a pioneering German physiologist whose groundbreaking work laid the foundation for our understanding of metabolism. Travel back to the 18th century when kidney stones puzzled scientists and sparked investigations into metabolic disorders. Marvel at artwork C013 / 4675 depicting thyroid anatomy, showcasing its crucial role in regulating metabolism and overall health. Delve deeper into molecular intricacies with an image of cytochrome b5 molecule C015 / 6696, unraveling its contribution to metabolic processes within cells. Witness SEM images capturing thyroid gland capillaries and blood vessels, highlighting their vital role in transporting hormones essential for metabolism regulation. Contemplate creation through a conceptual image that symbolizes how metabolism is at the core of life's energy flow. Explore mitochondria up close with SEM images that showcase their unique structures and emphasize their significance in powering cellular activities. Gain insight into human physiology with a diagram illustrating key organs involved in digestion and metabolism – liver, stomach, gallbladder, and pancreas working harmoniously together. Peer into DNA interactions as TFAM transcription factor bound to DNA C015 / 7059 reveals how genes are regulated to maintain optimal metabolic function within cells. Uncover the intricate relationship between thyroid and pituitary glands – two master regulators orchestrating hormonal balance crucial for proper metabolism control.