Mitochondria Collection (#5)
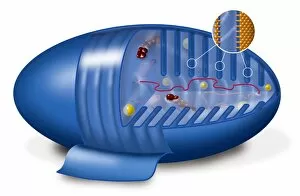
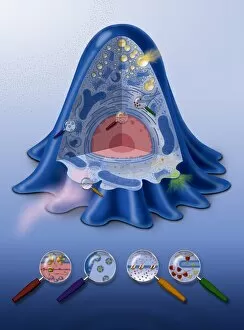
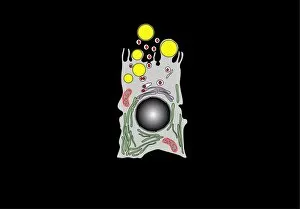
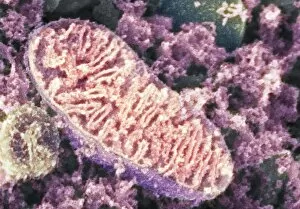
Mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, play a vital role in various organisms
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
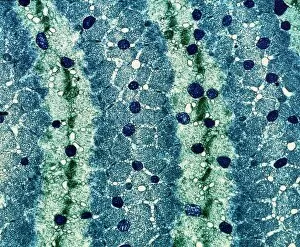
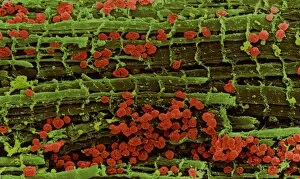
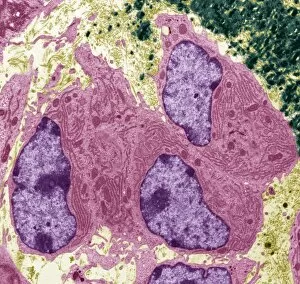
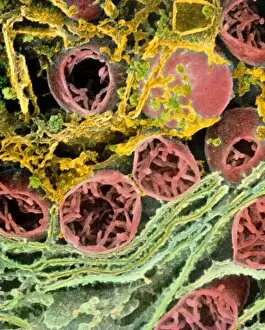
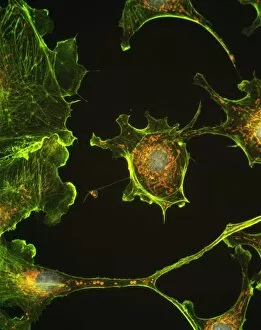
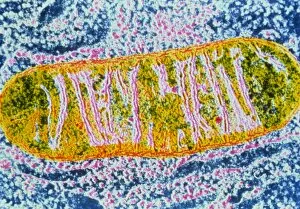
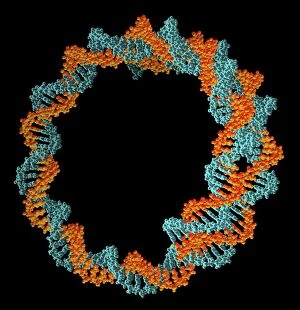
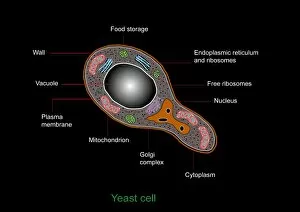
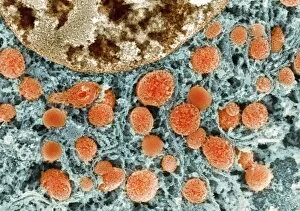
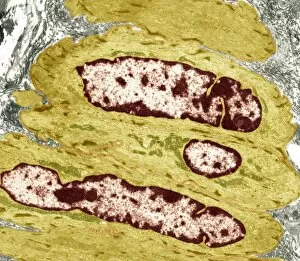
Mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, play a vital role in various organisms. From budding yeast cells to ovarian cells, their presence is visually striking under scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The colored SEM image in ovarian cells showcases their intricate structure and diversity across different cell types. In nerve cells, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) reveals the fascinating architecture of mitochondria. These elongated organelles are strategically positioned along axons and dendrites, ensuring efficient energy supply for neuronal functions. The TEM images capture the complexity and importance within nerve cells. Moving beyond nerve cells, plasma cells also exhibit distinct mitochondrial features when observed through TEM. These specialized immune system components rely on robust energy production to carry out antibody synthesis efficiently. Their unique morphology highlights how mitochondria adapt to meet specific cellular demands. The eye muscle's TEM image further emphasizes the significance in highly active tissues. With an abundance of these organelles, eye muscles can sustain continuous contractions required for precise vision movements. Macrophage cells also showcase intriguing mitochondrial structures when examined using TEM techniques. As key players in our immune defense system, macrophages require substantial energy reserves to engulf pathogens effectively. Mitochondrial dynamics contribute significantly to this process by providing ample ATP generation. Under SEM imaging techniques specifically focused on mitochondria themselves, their distinctive shape becomes apparent—ranging from elongated tubules to spherical forms that vary across species and tissue types. Understanding animal cell structure necessitates studying not only individual organelles but also their interactions with other cellular components like DNA-binding proteins such as TFAM transcription factor bound to DNA shown in C015 / 7059 micrograph. Exploring various microscopic views allows us to appreciate the remarkable diversity and essential roles played by mitochondria across different cell types and organisms alike—a testament to their fundamental significance within biological systems.