Mucosal Collection
"Mucosal: Unveiling the Intricate World of Our Body's Protective Lining" Our body is a complex system, and within it lies an intricate network known as mucosal lining
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
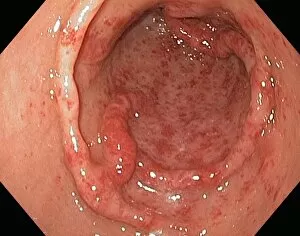
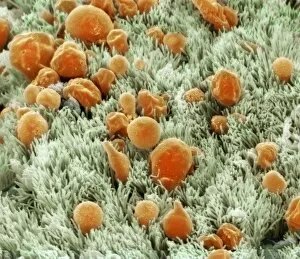
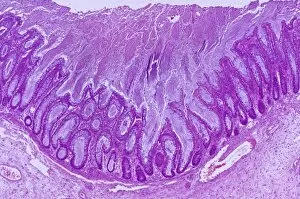
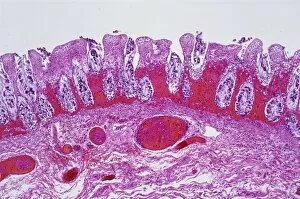
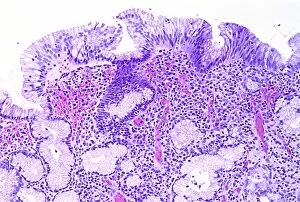
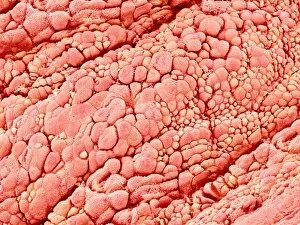
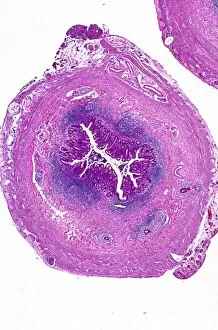
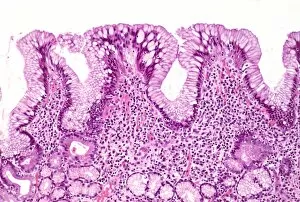
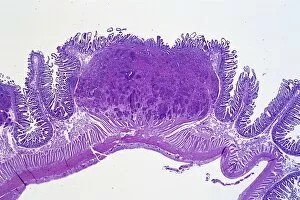
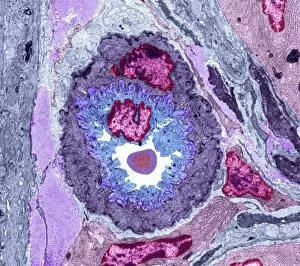
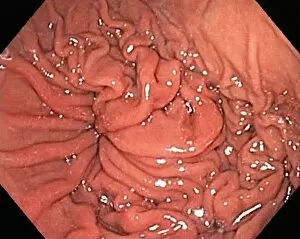
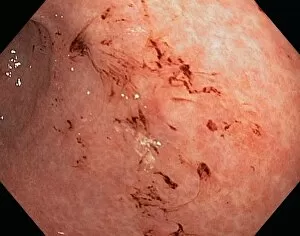
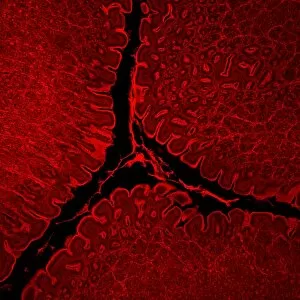
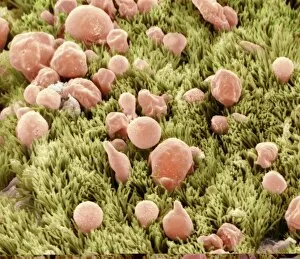
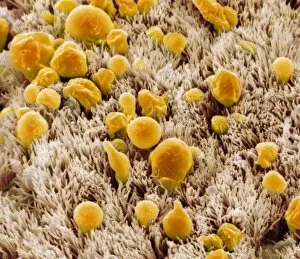
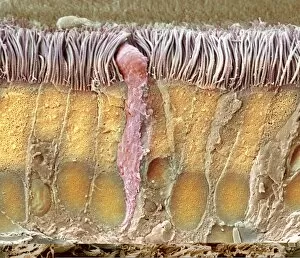
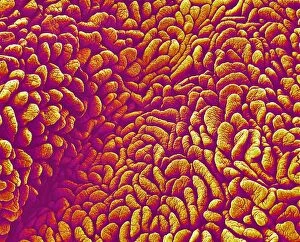
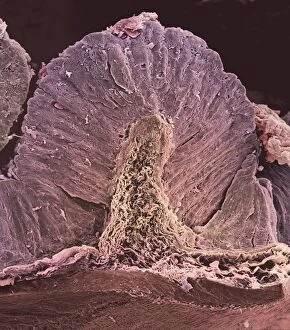
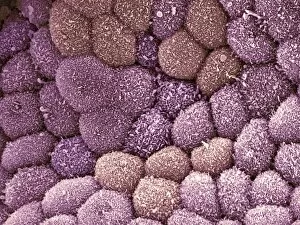
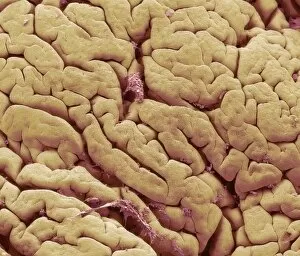
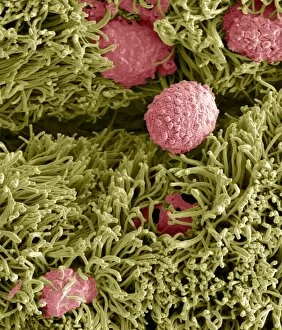
"Mucosal: Unveiling the Intricate World of Our Body's Protective Lining" Our body is a complex system, and within it lies an intricate network known as mucosal lining. This remarkable barrier plays a vital role in protecting various organs and tissues from harm. Let's delve into some fascinating glimpses of different mucosal regions: Gastric Antral Vascular Ectasia (GAVE) C016 / 8328: Explore the mesmerizing patterns formed by blood vessels in the stomach's antrum region, highlighting GAVE. Trachea Lining, SEM C013 / 7126: Witness the microscopic beauty of tracheal lining through scanning electron microscopy, revealing its delicate structure. SEM C013 / 7122: Another captivating view showcasing the intricacies of our respiratory system's protective layer - the tracheal lining. Ulcerative Pancolitis C018 / 0928: Observe how inflammation affects the entire colon with this image depicting ulcerative pancolitis, emphasizing mucosal damage. 5-7. Gastritis Light Micrograph (x3): Journey into gastric troubles with these light micrographs capturing gastritis - inflammation of stomach lining caused by various factors. 8-9. Colitis Light Micrograph (x2): Delve deeper into colonic health as these images portray colitis - inflammation affecting large intestine mucosa leading to discomfort. Ischaemic Bowel Light Micrograph: Witness how insufficient blood supply can impact bowel health through this enlightening light micrograph showcasing ischaemic bowel condition. 11-12. Vaginal Mucosa Light Micrograph (x2): Discover the importance of vaginal mucosa in maintaining reproductive health through these vivid light micrographs that unveil its unique characteristics.