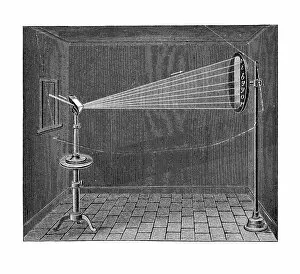
Optical Collection (#22)
"Exploring the Mysteries of the Optical Universe: From Orion Nebula to Northern Lights" Step into a world where beauty and wonder collide
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
"Exploring the Mysteries of the Optical Universe: From Orion Nebula to Northern Lights" Step into a world where beauty and wonder collide, as we delve into the captivating realm phenomena. The breathtaking Orion Nebula unveils its celestial secrets, showcasing a cosmic ballet of Blossom and Decay. Behold the mesmerizing Nebula Sh 2-106 in all its glory, captured by the Hubble Space Telescope's keen eye. Its ethereal hues paint an otherworldly canvas that transports us to distant galaxies. But it's not just far-off wonders that captivate our gaze; closer to home, nature puts on its own spectacular light show with the enchanting dance of the Northern Lights. A sight so magical, it leaves us awestruck at Earth's natural marvels. Through an optical lens, we peer into space and witness Sirius shining brightly amidst a sea of stars. The star filter reveals its true radiance, reminding us of our infinitesimal place in this vast universe. The spiral galaxy M81 beckons us further into deep space with its stunning composite image. Its swirling arms tell tales of cosmic evolution and remind us that even galaxies are subject to change. Venturing deeper still, we encounter the enigmatic Horsehead Nebula—a dark silhouette against a backdrop of stellar brilliance—an enigma waiting to be unraveled. Andromeda Galaxy awaits our exploration next—the closest spiral galaxy to our Milky Way—inviting us to ponder what lies beyond our familiar celestial neighborhood. Intriguingly intertwined within this tapestry is also human ingenuity—the University of Oxford's College serves as a cradle for knowledge seekers who unravel these mysteries day by day. Meanwhile, Chadburn Brothers' Albion Works stands as testament to humanity's pursuit in crafting precise optical instruments that unlock new realms for discovery.