Rameses Ii Collection (page 5)
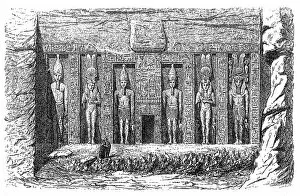
Rameses II, also known as Ramesses the Great, was one of ancient Egypt's most powerful pharaohs
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
Rameses II, also known as Ramesses the Great, was one of ancient Egypt's most powerful pharaohs. His legacy can be seen in various magnificent structures scattered across the country. One such structure is the Karnak Temple in Luxor, Egypt, where Rameses II left his mark for eternity. In a wood engraving published in 1881, we catch a glimpse of Ramesses III, who ruled from around 1221 BC to 1156 BC. This depiction gives us an insight into the regal and majestic appearance that characterized many Egyptian pharaohs. The Temple of Luxor itself houses a colossal statue of Rameses II. This awe-inspiring sculpture stands tall amidst the ruins and serves as a testament to his grandeur and influence over ancient Egypt. Another captivating image captures Ramses II alongside his daughter Bant Anta at the forecourt of the temple of Karnak. The bond between father and daughter is beautifully portrayed against this backdrop of architectural marvels. Moving further south to Abu Simbel, we encounter more statues and temples dedicated to Ramses II. The main chamber boasts intricate reliefs that depict scenes from his reign – a visual narrative frozen in time for all to admire. One cannot overlook Ramses II's iconic double crown depicted on various artifacts throughout history. Made from red and grey granite with an unknown provenance during the 19th dynasty, these crowns symbolize his authority over both Upper and Lower Egypt. Amongst these treasures lies an impressive obelisk dating back to 1193-1162 BC from Karnak. Carved out of granite, it stands tall as another reminder of Rameses' enduring presence within Egyptian history. A pink granite statue found in Tanis showcases Ramses II as a standard bearer during his reign – an embodiment of strength and leadership captured forever in stone. Two stunning red granite statues provide detailed glimpses into the pharaoh's likeness.