Sectioned Collection (#45)
"Exploring the Intricacies: From Cerebellum Tissue to Fusion Research, Unveiling the World Sectioned" Delving into the depths of scientific exploration
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
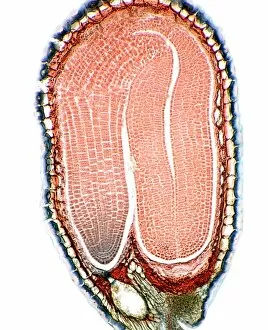
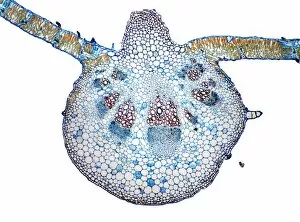
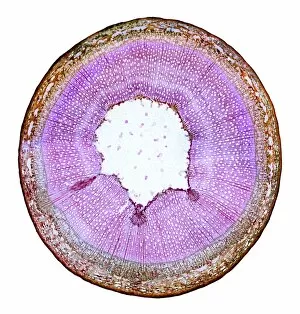
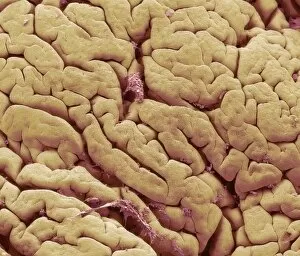
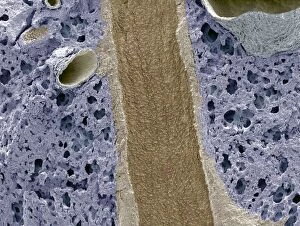
"Exploring the Intricacies: From Cerebellum Tissue to Fusion Research, Unveiling the World Sectioned" Delving into the depths of scientific exploration, a light micrograph reveals the intricate structure of cerebellum tissue. Witnessing a Higgs boson event through the lens of ATLAS detector C013/6892, scientists capture an awe-inspiring moment in particle physics. A meticulously crafted model showcases the complexity and beauty of the human brain, inviting us to marvel at its wonders. Peering into hippocampus brain tissue under a microscope, we uncover secrets that may hold keys to memory formation and learning processes. In pursuit of limitless energy sources, fusion research takes center stage as we examine a tokamak device designed for controlled nuclear fusion reactions. The inner workings of our brains come alive through an MRI scan, revealing detailed brain anatomy like never before imagined. Illuminated by light microscopy, dicotyledon plant stem sections unveil nature's architectural masterpiece in stunning detail. EDTA crystals take on mesmerizing patterns when viewed under intense magnification - showcasing their unique molecular arrangement through light micrography. Journeying deep within our bodies, kidney tubules are sectioned to shed light on their vital role in maintaining fluid balance and waste removal systems. An X-ray image exposes every contour and intricacy of a human skull – offering glimpses into our skeletal framework with remarkable clarity. Through transmission electron microscopy (TEM), rough endoplasmic reticulum emerges as an interconnected network responsible for protein synthesis within cells' cytoplasmic matrix Computer artwork visualizes Alzheimer's-affected brain regions – reminding us why continued research is crucial in unraveling this devastating disease. In this captivating journey across various scientific disciplines and microscopic landscapes, "sectioned" unveils hidden worlds that expand our understanding of the universe and ourselves.