Spore Collection (#5)
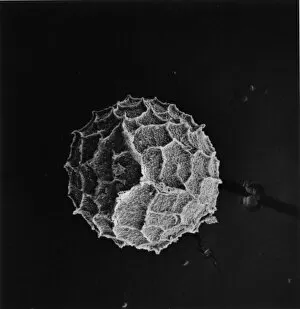
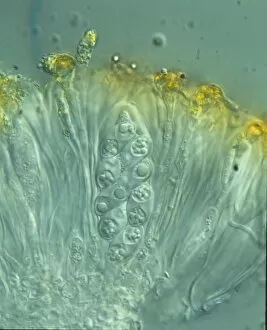
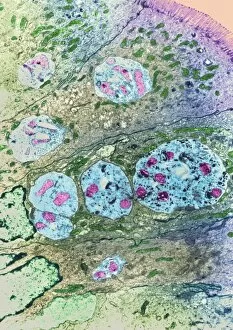
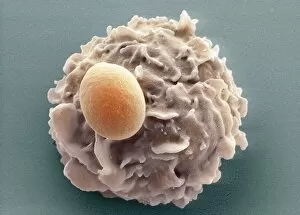
"Exploring the Fascinating World of Spores: From Aspergillus to Fungal Kingdom" Delving into the microscopic realm, we uncover the enchanting world of spores
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
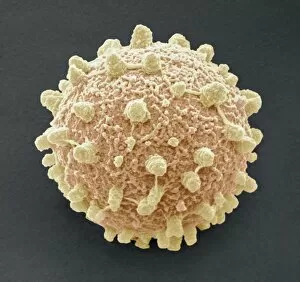
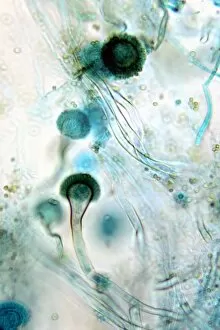
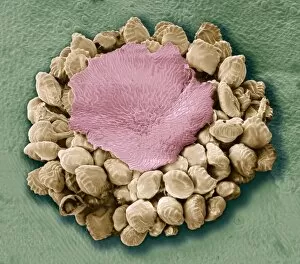
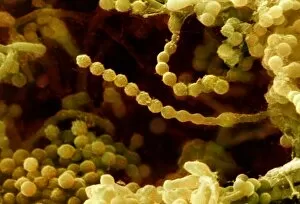
"Exploring the Fascinating World of Spores: From Aspergillus to Fungal Kingdom" Delving into the microscopic realm, we uncover the enchanting world of spores. Take a closer look at these tiny wonders that play a significant role in various organisms' life cycles. Intriguingly, Aspergillus reveals its intricate structure under scrutiny. Its delicate filaments intertwine, forming an elaborate network that aids in reproduction and dispersal. Moving on to moss capsules like Homalothecium sericeum, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) unveils their mesmerizing architecture. These capsules serve as nature's ingenious vessels for carrying spores, ensuring their propagation across vast distances. Witnessing phagocytosis of fungal spores through SEM is truly captivating. This process showcases how cells engulf these minuscule entities, highlighting the complex interactions between fungi and other organisms within ecosystems. Cyanobacteria also make an appearance under SEM's watchful eye. Their vibrant colors come alive as we observe these photosynthetic microorganisms responsible for oxygen production and nitrogen fixation. The horsetail family presents its own unique spore structures captured by SEM. The common horsetail displays its distinctive spore arrangement while field horsetail exhibits its elegant beauty up close - both showcasing nature's remarkable diversity. Bread mould takes center stage with SEM revealing its intricate filamentous hyphae adorned with countless reproductive spores. These resilient structures ensure bread mould's survival even in unfavorable conditions. Further exploring fungal realms through SEM unravels more astonishing details about their diverse forms and functions. Each species boasts distinct characteristics that aid them in colonizing new habitats or spreading far and wide across landscapes. Clostridium tetani offers us a glimpse into history with an ancient lithograph depicting colonies brimming with dormant yet potent spores dating back to 1906 – reminding us of science's enduring quest to understand the microbial world.