Stigma Collection (#8)
"Breaking the Chains: Unraveling the Stigma Surrounding Nature's Wonders" In Saint Joseph of Cupertino's Ecstasy
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
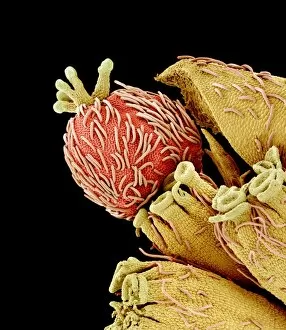
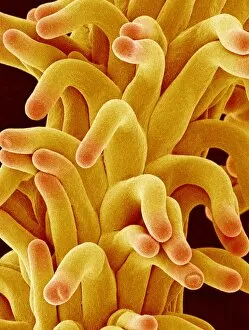
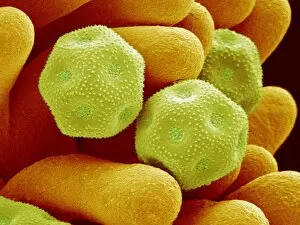
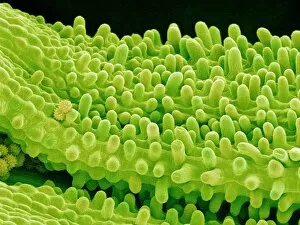
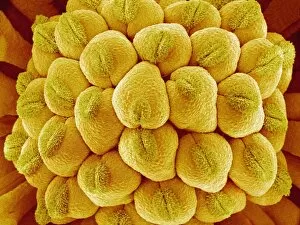
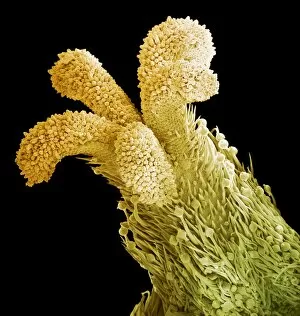
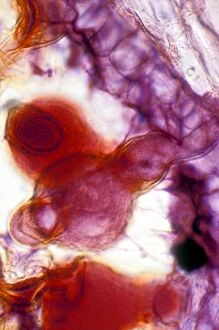
"Breaking the Chains: Unraveling the Stigma Surrounding Nature's Wonders" In Saint Joseph of Cupertino's Ecstasy, we witness a divine connection that transcends human understanding. Just like this masterpiece, stigma in nature holds profound significance. The Methodus plantarum sexalis in sistemate naturae descripta reveals the intricate classification of plants, shedding light on how stigma plays a vital role in their reproductive processes, and is through these delicate structures that life perpetuates itself. Zooming into an Easter cactus stigma under SEM, we discover its mesmerizing beauty up close. The Studio shot captures the essence of a pink tulip flower with such precision that we can almost feel its velvety touch. Morning glory pollen captured by SEM showcases the interplay between stigma and pollen grains—a dance essential for successful pollination. Similarly, Gorse stigma adorned with pollen grains exemplifies nature's harmonious collaboration to ensure survival. A False-colour SEM image of chickweed flower reminds us that even seemingly insignificant flora possess unique stigmas worthy of admiration. Each microscopic detail tells a story waiting to be unraveled. Pollination takes center stage as different species intertwine their destinies through this sacred union. Amaryllis stands tall as Hippeastrum sp. , showcasing vibrant stigmas inviting pollinators to partake in their splendorous feast. Traveling to Greece, we encounter Saffron Crocus—its precious saffron harvested from meticulously hand-picked stigmas—an ancient tradition steeped in culture and history. Lastly, Thale cress flower micrograph serves as a testament to scientific exploration; it invites us into its miniature world where every aspect contributes to our understanding of life's intricacies. Through these captivating glimpses into nature's wonders, let us challenge societal norms and break free from the chains of prejudice surrounding "stigma. " May we recognize its inherent beauty and importance, both in art and the natural world.