Tertiary Structure Collection (#7)
Tertiary structure is a fascinating aspect of molecular biology that plays a crucial role in the functionality and stability of various biological molecules
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
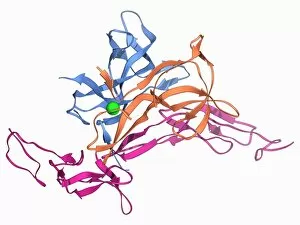
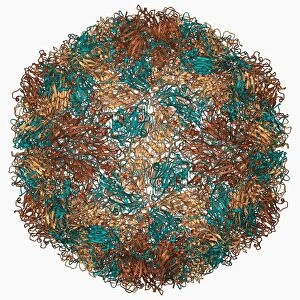
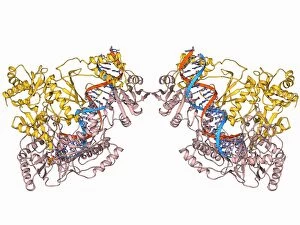
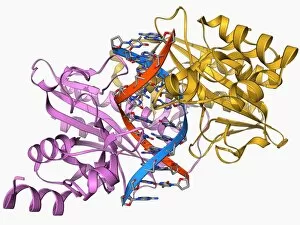
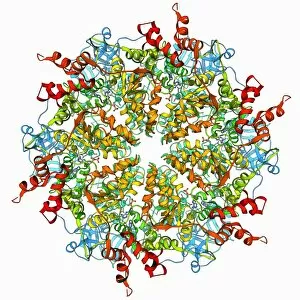
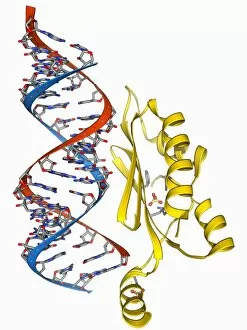
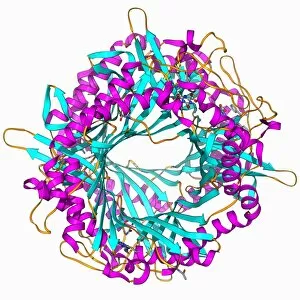
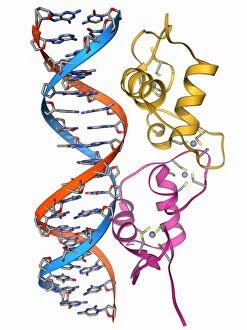
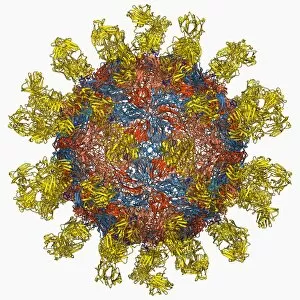
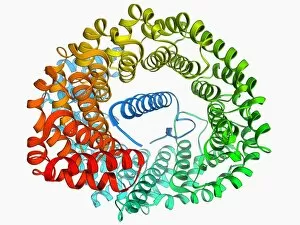
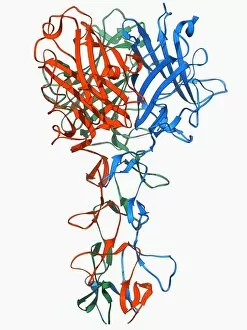
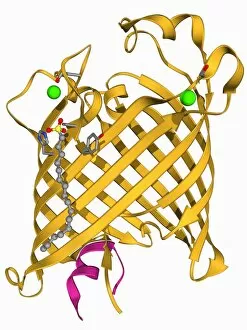
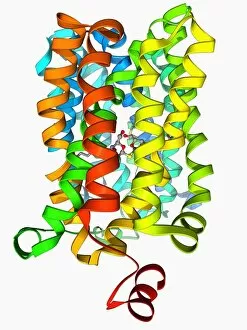
Tertiary structure is a fascinating aspect of molecular biology that plays a crucial role in the functionality and stability of various biological molecules. One such example is the Manganese superoxide dismutase enzyme F006 / 9423, which possesses an intricate tertiary structure that allows it to efficiently scavenge harmful reactive oxygen species. Another intriguing molecule with a well-defined the Argonaute protein F006 / 9526. This protein acts as a key component of RNA-induced silencing complex F006 / 9586, enabling it to bind microRNAs and regulate gene expression through post-transcriptional mechanisms. The Immunoglobulin G antibody and egg white F006 / 9682 exhibit an interesting interaction where the tertiary structure of the antibody enables it to recognize specific antigens present in egg white, triggering an immune response. Cytochrome P450 complex F006 / 9669 showcases how multiple proteins come together to form a functional unit responsible for metabolizing drugs and toxins in our bodies. The precise arrangement of these proteins within their tertiary structures ensures efficient catalytic activity. Succinyl-CoA synthetase enzyme F006 / 9592 participates in the citric acid cycle (also known as Krebs cycle) by converting succinyl-CoA into ATP. Its unique tertiary structure facilitates substrate binding and enzymatic reactions essential for energy production. Viruses also possess captivating tertiary structures; one example being Foot-and-mouth disease virus F006 / 9556. Understanding its intricate capsid architecture aids researchers in developing effective vaccines against this highly contagious viral infection. Adenovirus penton base protein F006 / 9542 exhibits an elaborate tertiary structure critical for viral entry into host cells during infection. Studying this protein's conformation provides insights into potential therapeutic targets against adenoviral infections. Rhinovirus 16 capsid, molecular model F006/9431 represents another virus with a well-characterized tertiary structure.