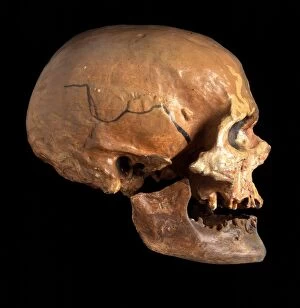
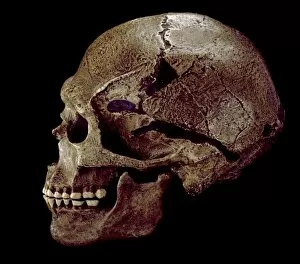
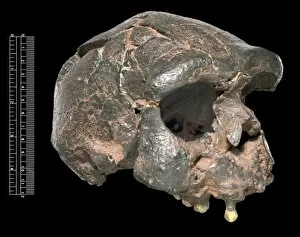
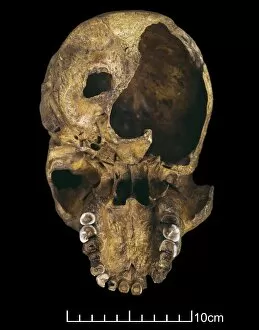
Anthropological Collection (#6)
"Unveiling the Secrets of our Ancestors: Exploring Anthropological Treasures" Step into the captivating world of anthropology as we embark on a journey through time
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
"Unveiling the Secrets of our Ancestors: Exploring Anthropological Treasures" Step into the captivating world of anthropology as we embark on a journey through time. From the mesmerizing Lascaux II cave painting replica to the enigmatic Stone-age cave paintings in Chauvet, France, these ancient artworks offer us a glimpse into humanity's past. Delve deeper and encounter the Cave of Hands in Argentina, where handprints left by our ancestors thousands of years ago continue to intrigue and mystify. These imprints serve as a testament to their existence and leave us pondering about their lives. As we shift our focus from art to anatomy, hominid crania take center stage. The Australopithecus afarensis (AL 288-1), fondly known as Lucy, stands tall among her counterparts. Her fossilized remains provide valuable insights into early human evolution and ignite curiosity about our own origins. But it doesn't stop there; prehistoric tools like spear-throwers remind us of our ancestors' resourcefulness and ingenuity. These artifacts shed light on how they survived and thrived in challenging environments. And let's not forget the Laetoli fossil footprints that tell an extraordinary story etched in volcanic ash. Preserved for millions of years, these footprints capture moments frozen in time – evidence of bipedal locomotion long before modern humans roamed the Earth. Returning once again to Chauvet, France, stone-age cave paintings continue to captivate with their intricate details and symbolic representations. Each stroke carries whispers from those who came before us – messages waiting patiently for interpretation. Finally, we encounter the Venus of Brassempouy – an exquisite ivory figurine representing fertility or perhaps even spirituality. This timeless masterpiece reminds us that throughout history, humans have sought meaning beyond survival alone. Anthropology unravels stories hidden within these remarkable artifacts – stories of resilience, creativity, and the unending quest for knowledge.