Biochemical Collection (#85)
"Unveiling the Intricacies of Biochemical World: From Anaesthetic Inhibiting Ion Channels to DNA Discoveries" Delving into the depths wonders
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
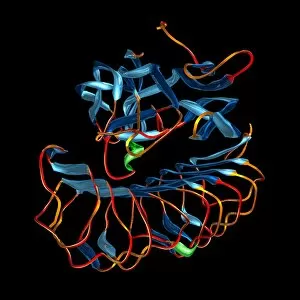
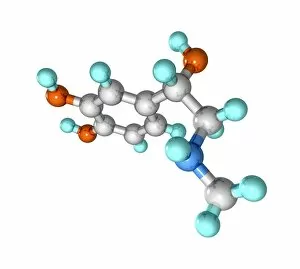
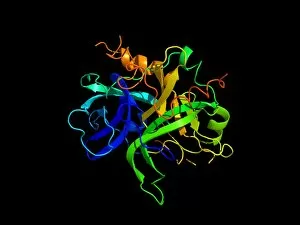
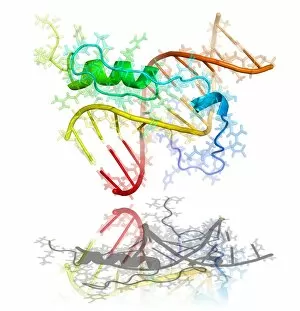
"Unveiling the Intricacies of Biochemical World: From Anaesthetic Inhibiting Ion Channels to DNA Discoveries" Delving into the depths wonders, scientists have uncovered an anaesthetic that inhibits an ion channel (C015 / 6718), shedding light on new possibilities for pain management. The enigmatic double-stranded RNA molecule reveals its secrets, captivating researchers with its role in gene regulation and potential therapeutic applications. Peering into the intricate world of DNA transcription through a molecular model, scientists unravel the mysteries behind genetic information transfer and cellular function. Captured under a microscope's gaze, caffeine crystals dazzle with their vibrant beauty, reminding us of this ubiquitous stimulant's impact on our daily lives. The iconic DNA molecule stands tall as a symbol of life's blueprint, holding within it the key to our genetic heritage and evolutionary history. Immunoglobulin G antibody molecule emerges as a formidable defender against pathogens, showcasing nature's ingenious immune system at work. Through mesmerizing crystal formations seen under intense magnification, EDTA crystals reveal their significance in chelation therapy and metal ion sequestration processes. Oxytocin hormone crystals shimmer like precious gems when observed through polarized light microscopy (PLM C016 / 7196), highlighting its crucial role in social bonding and reproductive functions. Watson and Crick forever etched their names in scientific history by unravelling the structure of DNA; their groundbreaking discovery paved the way for countless advancements in genetics research. Celebrated author Isaac Asimov not only captivated readers with his science fiction tales but also left an indelible mark as a biochemist who popularized complex scientific concepts for all to comprehend and appreciate. Artistic renditions bring metabolic enzymes to life as they orchestrate vital chemical reactions within cells – true catalysts that drive life's intricate processes.