Cell Collection (#97)
"Exploring the Intricacies of Life: Unveiling the Wonders of Cells" Delving into the microscopic world
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
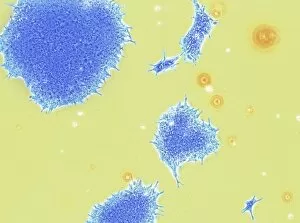
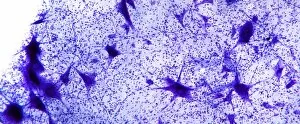
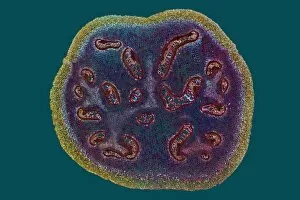
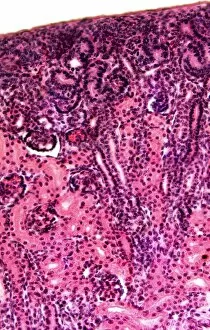
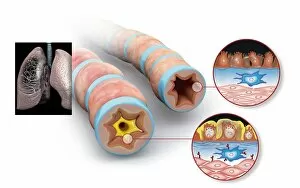
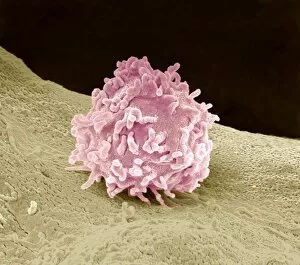
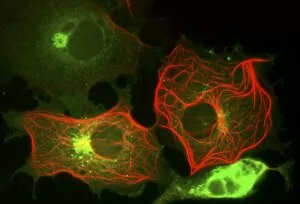
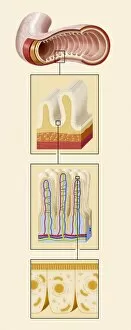
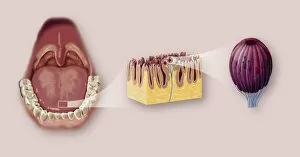
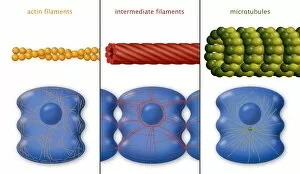
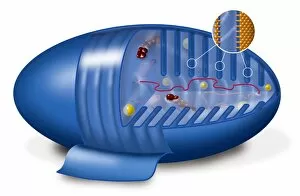
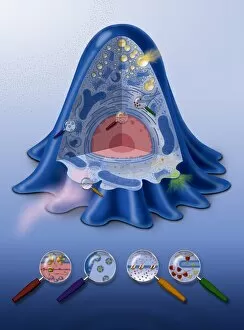
"Exploring the Intricacies of Life: Unveiling the Wonders of Cells" Delving into the microscopic world, a histological diagram of a mammalian retina reveals the intricate structure and organization of cells that enable us to perceive light. The cerebellum tissue, captured in a light micrograph, showcases its complex network of cells responsible for coordinating movement and balance. Intriguingly, even philosophers find solace in contemplating cellular existence. "Philosopher in Meditation, " an oil painting from 1632, reminds us that pondering life's mysteries often leads us back to our fundamental building blocks – cells. Zooming further into this realm, nerve and glial cells come alive under the lens. This captivating light micrograph highlights their vital role in transmitting signals throughout our nervous system. Meanwhile, a lavender pollen grain captured through scanning electron microscopy (SEM) displays nature's exquisite design at the cellular level. The battle against diseases takes center stage as T lymphocytes confront cancer cells in another SEM image. Science and evolution intertwine as we witness these tiny warriors fighting for survival within our bodies. Artistic expressions also shed light on cell significance; "The Death of Socrates, " painted in 1787, serves as a poignant reminder that even great minds are ultimately composed of countless individual cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal's meticulous drawing from 1894 unveils various cell types within the mammalian cerebellum. His work not only represents scientific progress but also exemplifies how art can aid understanding by visually capturing complexity. Stepping away from biology momentarily, we encounter Rolls Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 Mk602 engine undergoing testing within a controlled environment called a test cell. Here too, precision engineering relies on understanding cellular mechanics to achieve optimal performance. Returning to biological marvels - HeLa cells take center stage under yet another microscope lens. These immortalized human cells have revolutionized medical research, paving the way for countless breakthroughs.