Histology Collection (#10)
Histology, the study of tissues at a microscopic level, unveils the intricate beauty and complexity of our body's structures
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
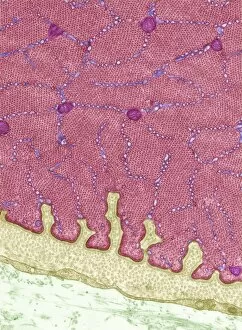
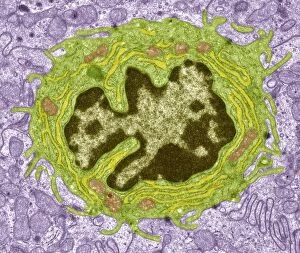
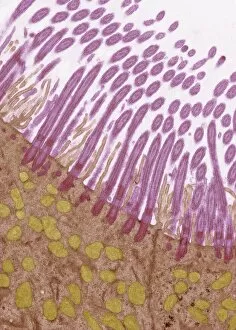
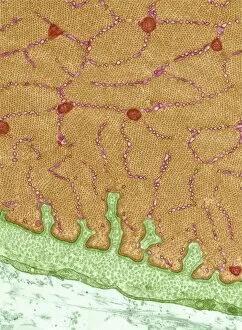
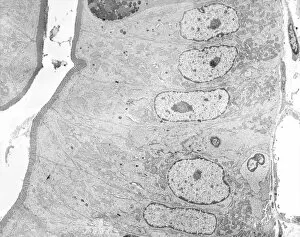
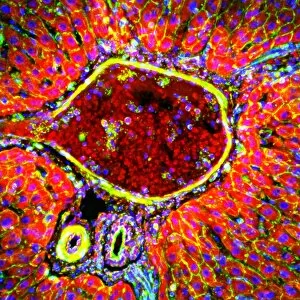
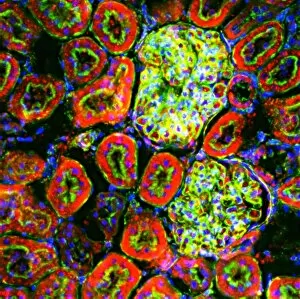
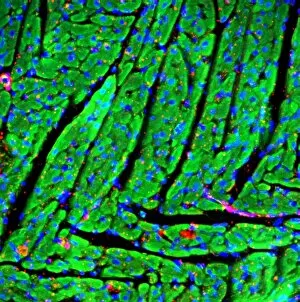
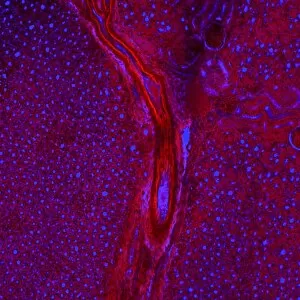
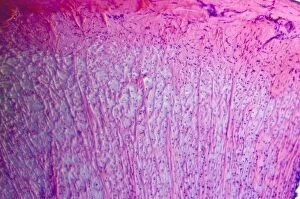
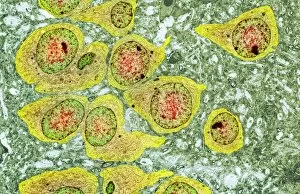
Histology, the study of tissues at a microscopic level, unveils the intricate beauty and complexity of our body's structures. Through techniques like light micrography and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scientists have been able to explore various tissues and unravel their secrets. One such tissue is the cerebellum, which plays a crucial role in coordinating movement and balance. By examining cerebellum tissue under a light microscope, we can observe its distinct layers and cell types. The synapse nerve junctions captured through TEM reveal the precise connections between neurons that allow for seamless communication. In 1894, Spanish histologist Santiago Ramon y Cajal created an exquisite drawing showcasing different cell types within the mammalian cerebellum. His meticulous work laid the foundation for understanding neural networks. Moving beyond just one region of the brain, histologists also delve into other fascinating areas like the hippocampus. Microscopic examination of hippocampus brain tissue provides insights into memory formation and spatial navigation. Purkinje nerve cells found within the cerebellum are particularly captivating under scrutiny. Their elaborate branching patterns give rise to their unique appearance when observed through a microscope slide. Histological studies extend beyond neurological tissues; they encompass organs throughout our body systems as well. For instance, kidney tubules in section offer glimpses into renal function while highlighting their structural organization. The human brain itself holds countless mysteries waiting to be unraveled by histologists examining microscope slides containing delicate slices of this complex organ. These slides provide glimpses into both healthy brains and those affected by diseases like Alzheimer's - offering valuable insights into neurodegenerative disorders. Exploring deeper with TEM reveals cellular components such as rough endoplasmic reticulum - an organelle involved in protein synthesis - providing detailed views at nanoscale resolution. Histology not only focuses on neurons but also encompasses glial cells that support neuronal functions. Light micrographs capturing glial stem cell cultures showcase the potential for regeneration and repair within the nervous system.