Immunology Collection (page 9)
"Unleashing the Power of Immunology: Exploring the Intricate World of Immune Responses" Immunology
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
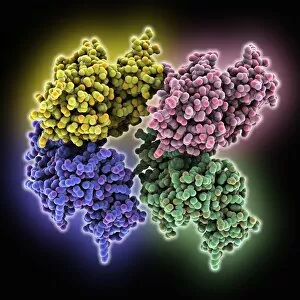
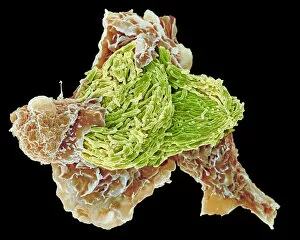
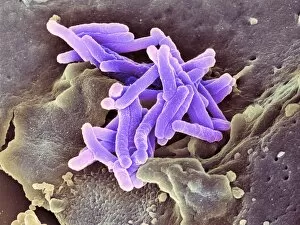
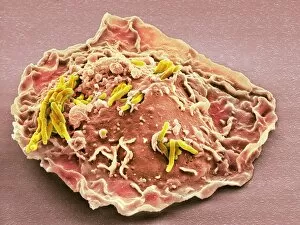
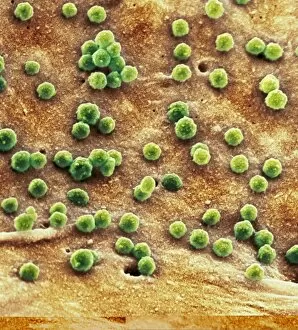
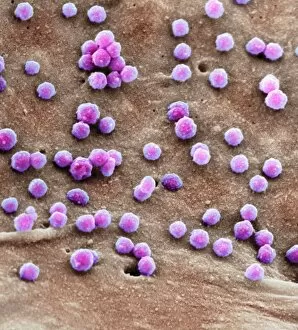
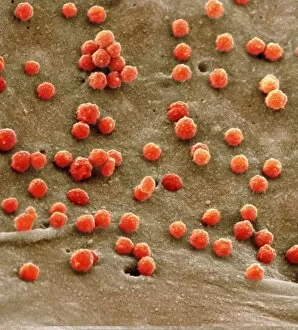
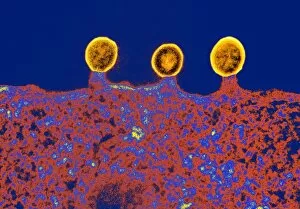
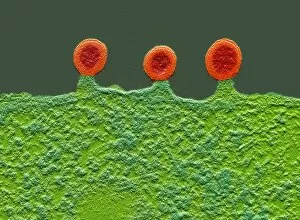
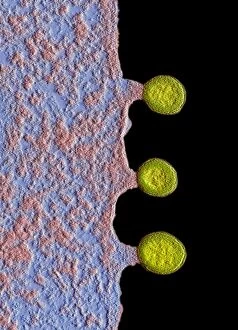
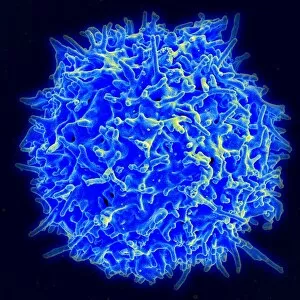
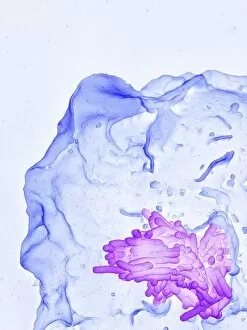
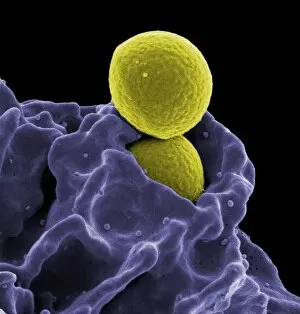
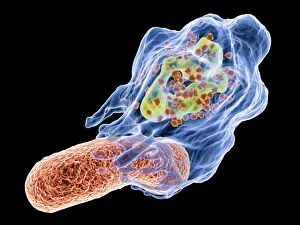
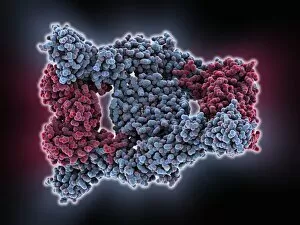
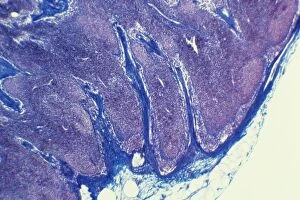
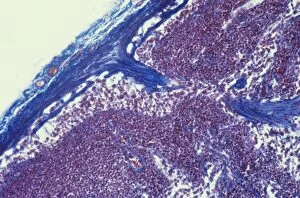
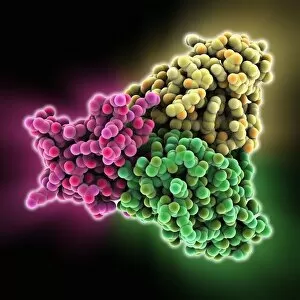
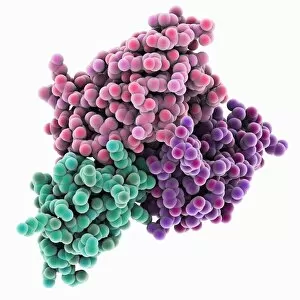
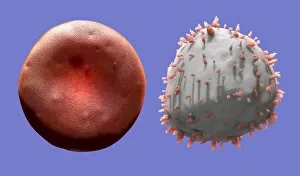
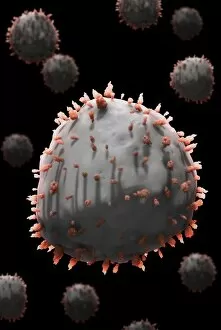
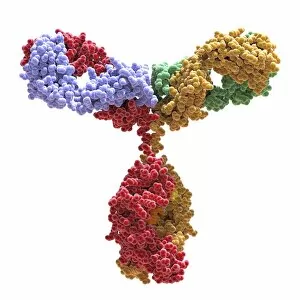
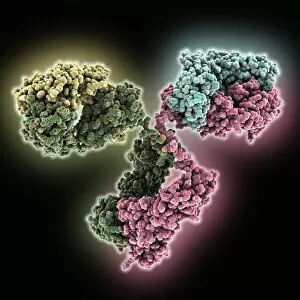
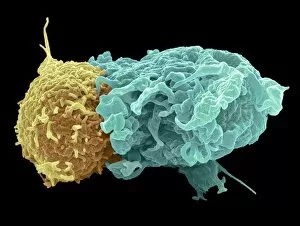
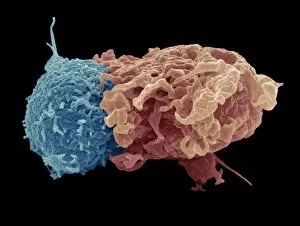
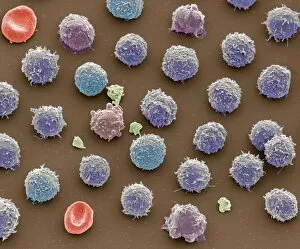
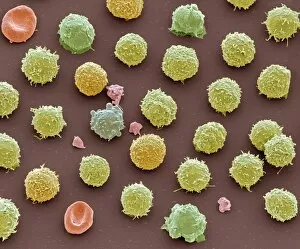
"Unleashing the Power of Immunology: Exploring the Intricate World of Immune Responses" Immunology, a fascinating field that delves into the complex mechanisms of our immune system, holds immense potential in combating diseases. T lymphocytes and cancer cells engage in a constant battle for supremacy, as depicted by SEM C001 / 1679. These tiny warriors play a crucial role in identifying and eliminating abnormal cells. The Immunoglobulin G antibody molecule (F007 / 9894) stands tall as one of our body's most powerful defenders against pathogens. Its remarkable structure enables it to neutralize harmful invaders with precision and efficiency. Neutrophils, exemplified by SEM C018 / 8596, showcase their extraordinary ability to engulf MRSA bacteria—an awe-inspiring sight indeed. Meanwhile, dendritic cells (artwork) act as vigilant sentinels, capturing antigens and presenting them to other immune cells for recognition. TEM reveals an up-close view of human white blood cells bearing HLA antigens—a key component in distinguishing self from non-self. Antibodies (artwork), resembling elegant warriors on a mission, bind specifically to foreign substances to mark them for destruction. HIV reverse transcription enzyme serves as a reminder of the challenges faced by immunologists worldwide. This relentless virus exploits our own cellular machinery but continues to be targeted through innovative research efforts. Human macrophages (TEM) demonstrate their exceptional phagocytic abilities while basophil white blood cells stand ready at the frontlines—both integral players in mounting effective immune responses against invading pathogens. Intriguingly captured by SEM imagery is bacteria infecting a macrophage—a visual representation highlighting how these microscopic organisms can exploit host defenses while also serving as valuable tools for studying infection dynamics. Lastly, Dohle bodies within blood cells offer insights into various pathological conditions affecting neutrophils—an essential clue guiding immunologists towards understanding and treating immune disorders.