Macromolecule Collection (#8)
Macromolecules, the building blocks of life, are at the forefront of scientific innovation
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
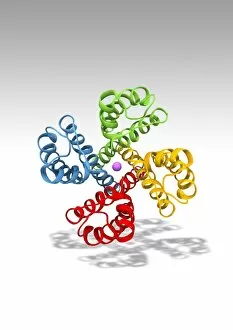
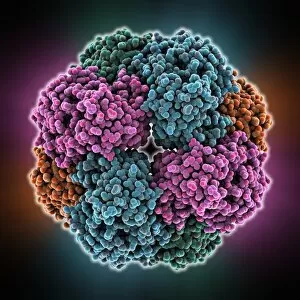
Macromolecules, the building blocks of life, are at the forefront of scientific innovation. Nanotube technology has revolutionized various fields, enabling advancements in medicine and electronics. In this captivating computer artwork, we witness the intricate Zinc fingers binding to a DNA strand, showcasing their crucial role in gene regulation. Carbon nanotubes have also emerged as remarkable materials with immense potential. Their unique structure and properties make them ideal for applications ranging from energy storage to drug delivery systems. Computer-generated images depict these carbon nanotubes in all their glory. The SARS coronavirus protein is another macromolecule that has garnered significant attention due to its role in viral infection. Scientists tirelessly study it to develop effective treatments against deadly outbreaks. Computer models allow us to explore complex structures like Bacteriophage phi29—a virus that infects bacteria—providing insights into its mechanisms and aiding in the development of targeted therapies. Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), closely related to HIV, poses a global health challenge. Understanding its macromolecular components helps researchers devise strategies for prevention and treatment. Rhodopsin protein molecule captures our imagination with its vital function in vision. Its elegant structure enables light detection and initiates visual signals within our eyes. TFAM transcription factor bound to DNA C015/7059 showcases how macromolecules regulate gene expression by interacting with specific regions on DNA strands—an essential process for cell functioning and development. These glimpses into the world of macromolecules highlight their significance across diverse disciplines—from cutting-edge technologies like nanotube engineering to unraveling infectious diseases or understanding fundamental biological processes. As scientists continue exploring these fascinating molecules, they pave the way for groundbreaking discoveries that shape our future.