Nerve Cell Collection (#5)
The intricate world of nerve cells, also known as neurons, is a fascinating realm within our bodies
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
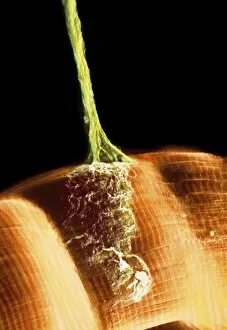
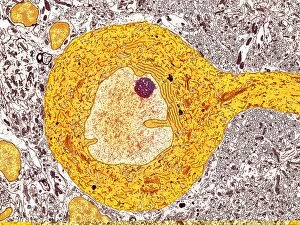
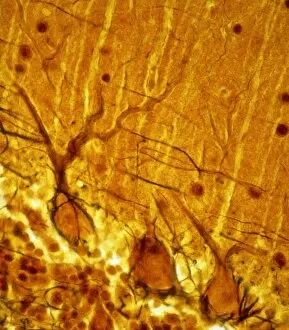
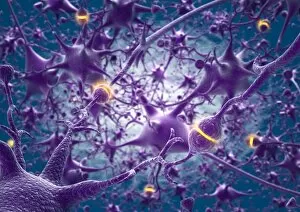
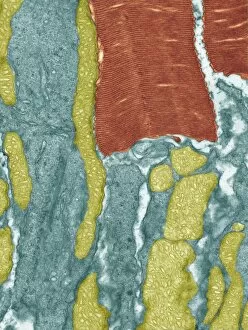
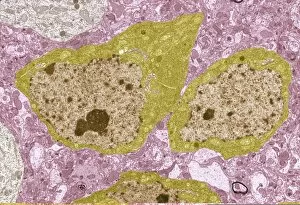
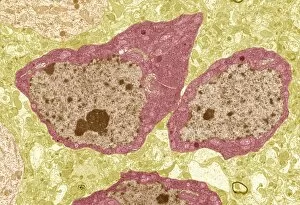
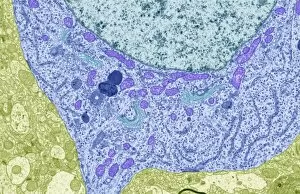
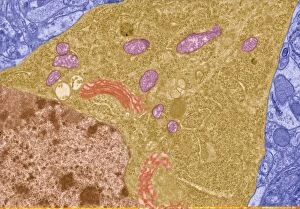
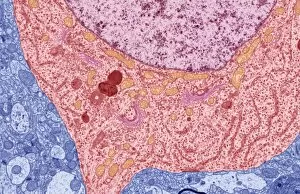
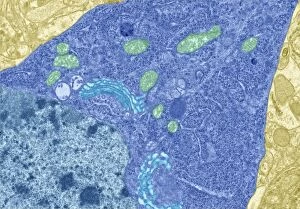
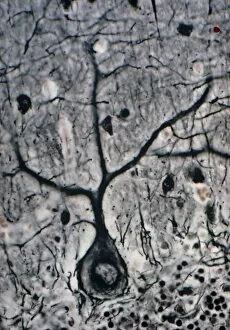
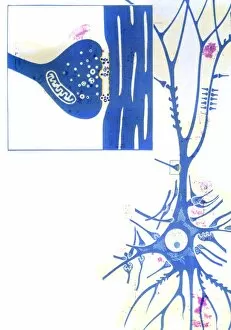
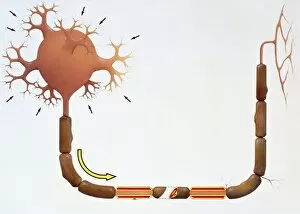
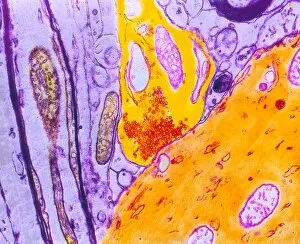
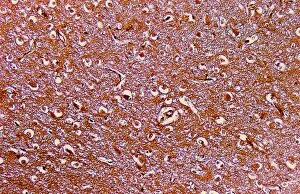
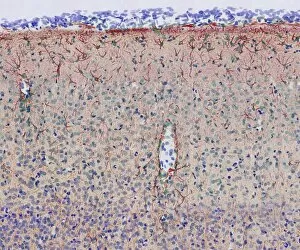
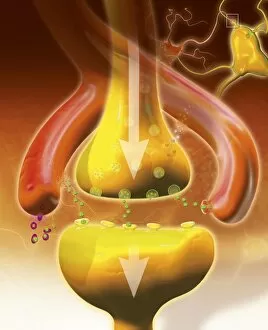
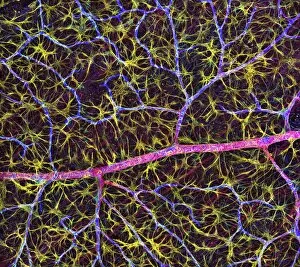
The intricate world of nerve cells, also known as neurons, is a fascinating realm within our bodies. These specialized cells play a crucial role in transmitting information throughout the nervous system. In the cerebellum tissue, under the lens of a light micrograph, we can observe the complex network formed by nerve and glial cells. This interplay between different cell types ensures proper functioning and communication within this region of the brain. Zooming in further with a transmission electron microscope (TEM), we witness the mesmerizing synapse nerve junctions - where two nerve cells meet to exchange vital signals. The intricacy of these connections highlights their importance in relaying messages across our neural pathways. Switching gears to scanning electron microscopy (SEM), we get an up-close look at individual nerve cells themselves. Their elongated structures and branching extensions showcase their ability to transmit electrical impulses efficiently. Moving on to hippocampus brain tissue, another essential area for memory formation and learning, we encounter Purkinje nerve cells nestled within the cerebellum. These large neurons have distinctive dendritic trees that receive inputs from various sources, contributing to motor coordination. As we explore further into brain tissue's complexity, it becomes evident that blood supply plays a crucial role in nourishing these delicate neural networks. A healthy flow ensures optimal functioning of all interconnected regions. Venturing beyond natural tissues into neural stem cell culture reveals exciting possibilities for regenerative medicine and understanding neurodevelopmental processes better. These cultured stem cells hold immense potential for repairing damaged nerves or studying neuronal growth patterns. Finally, let us not forget about cerebral cortex nerve cells - responsible for higher cognitive functions such as perception and decision-making. Their intricate arrangements enable us to process information effectively while navigating through daily life challenges. Whether observing cerebellum tissue or exploring neural stem cell cultures or marveling at synaptic connections under various microscopes – each glimpse into the world of nerve cells unveils new layers of complexity and highlights their indispensable role in our intricate neural symphony.