Organelle Collection (#2)
Organelles: The Tiny Powerhouses Within Our Cells The world of cells is a fascinating one, filled with intricate structures known as organelles
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
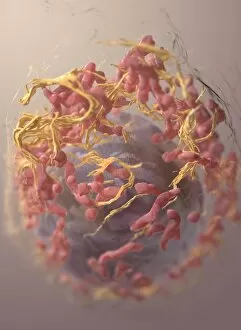
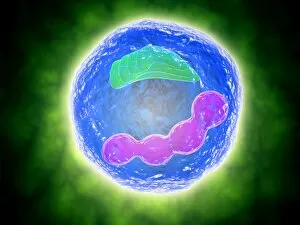
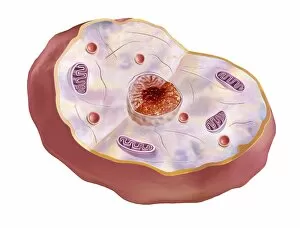
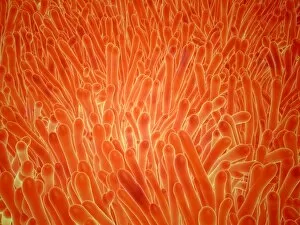
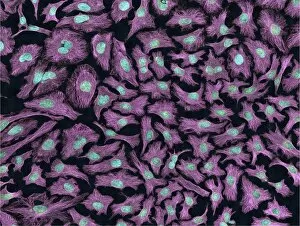
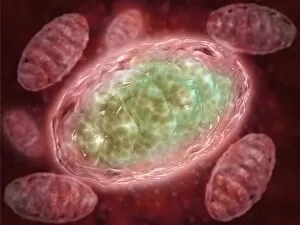
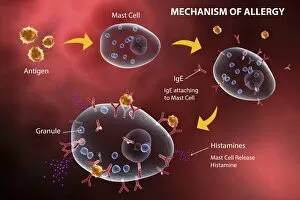
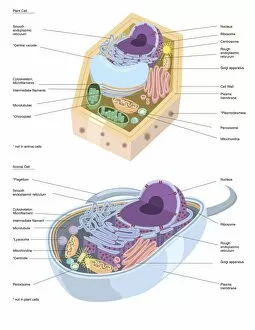
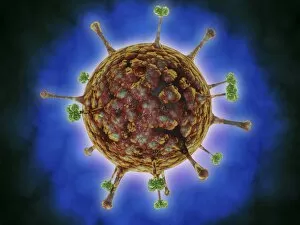
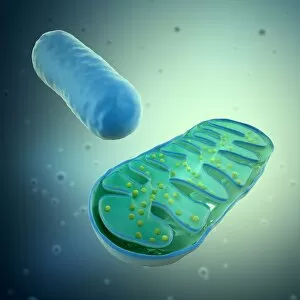
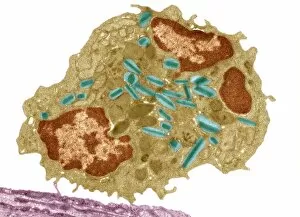
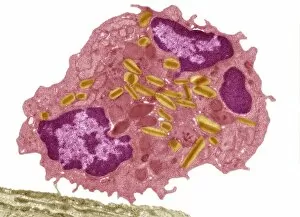
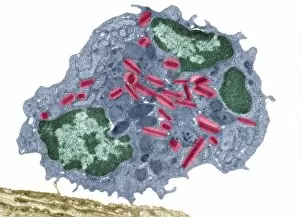
Organelles: The Tiny Powerhouses Within Our Cells The world of cells is a fascinating one, filled with intricate structures known as organelles. These tiny entities play crucial roles in maintaining the functionality and survival of our cells. From budding yeast to HeLa cells, each cell type possesses its unique set of organelles that contribute to their specialized functions. Under the lens of a light microscope, the HeLa cells reveal mesmerizing patterns resembling abstract artwork. Their delicate structures are visible, showcasing the complexity within these microscopic powerhouses. Meanwhile, another image captures nerve cells in all their glory - long and slender extensions reaching out like branches from a tree. Zooming in further using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), we get an up-close look at some specific organelles. The rough endoplasmic reticulum appears as a network of interconnected membranes studded with ribosomes responsible for protein synthesis. Mitochondria steal the spotlight next; these bean-shaped powerhouses generate energy for cellular activities through respiration. But it's not just animal cells that possess remarkable organelles; plant cells have their own unique features too. Chloroplasts, depicted beautifully through artwork, capture sunlight and convert it into energy via photosynthesis—a process vital for sustaining life on Earth. Another TEM image reveals Purkinje nerve cells—large neurons found in our brain's cerebellum—showcasing their intricate branching structure responsible for coordinating movement and balance. Finally, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) unveils the Golgi apparatus—an organelle involved in processing proteins and packaging them into vesicles for transportation throughout the cell or secretion outside it. These glimpses into different types of organelles highlight their diverse forms and functions within our cellular world. They remind us that even though they may be invisible to the naked eye, these minuscule entities hold immense importance in keeping our bodies functioning harmoniously at every level.