Phloem Collection (#4)
Phloem, the intricate network of vascular bundles responsible for transporting nutrients and sugars throughout plants, is a fascinating subject to explore
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
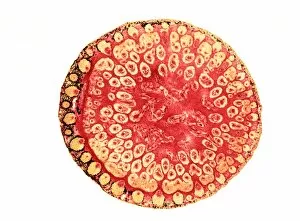
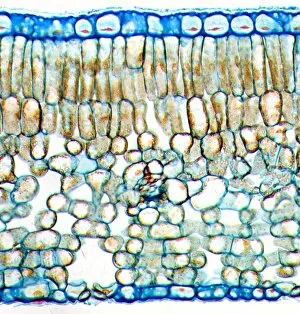
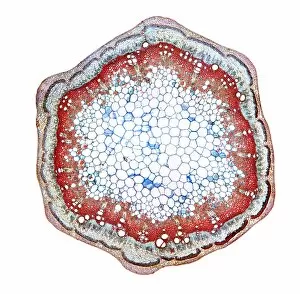
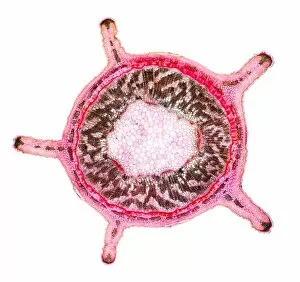
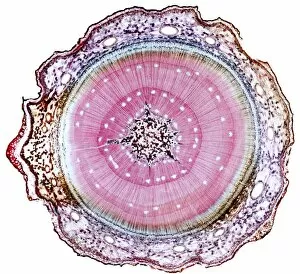
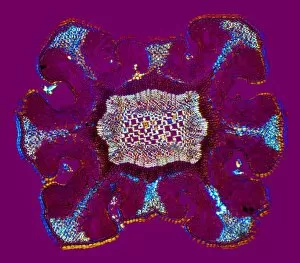
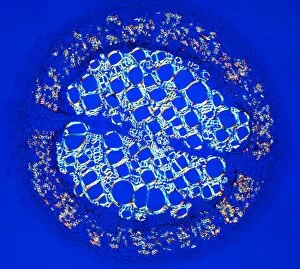
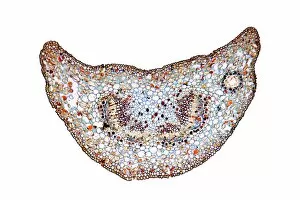
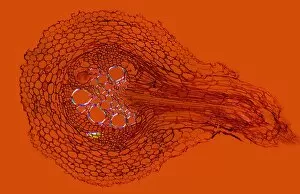
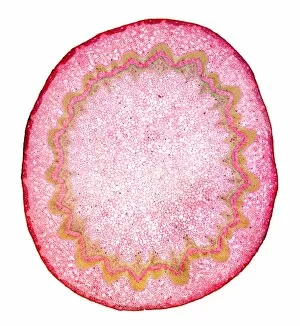
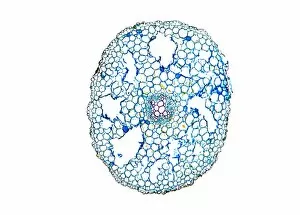
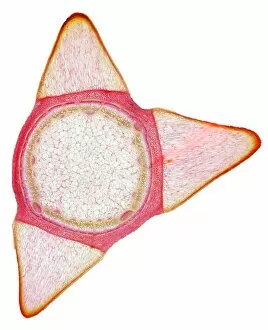
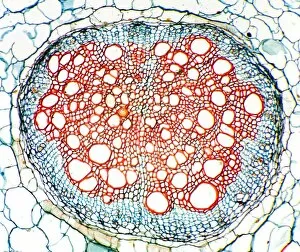
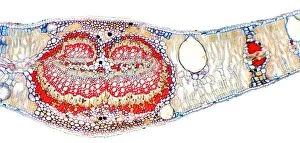
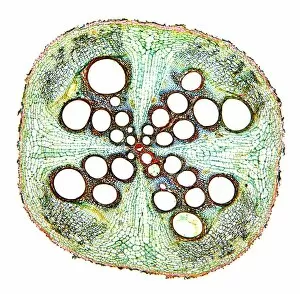
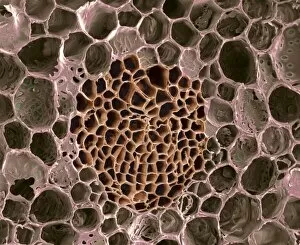
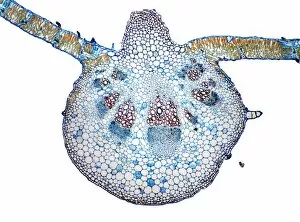
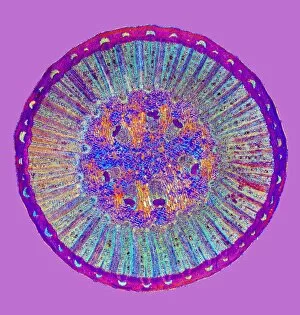
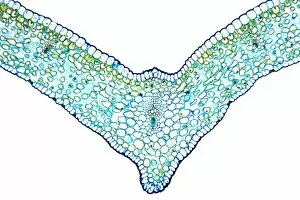
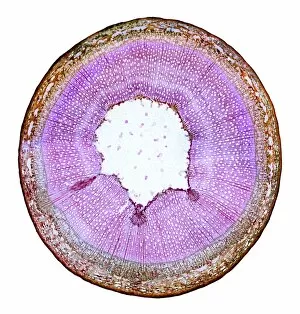
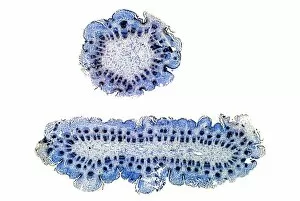
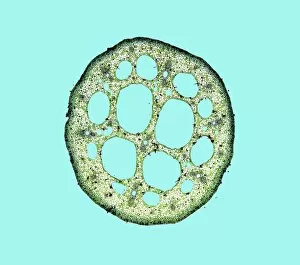
Phloem, the intricate network of vascular bundles responsible for transporting nutrients and sugars throughout plants, is a fascinating subject to explore. Through scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and light micrographs, we can delve into the hidden world in various plant species. In a lime tree stem, a light micrograph reveals the delicate structure cells intertwined within the vascular bundle. These specialized cells form sieve tubes that efficiently transport organic compounds from leaves to other parts of the plant. Similarly, in a maize root captured under a light microscope, we witness the intricate web-like arrangement tissue. This vital system ensures essential nutrients are distributed from roots to shoots for growth and development. The water lily leaf showcases another mesmerizing view through a light micrograph. Here, we observe elongated phloem fibers running parallel to each other like veins on this aquatic beauty's surface. Switching gears to SEM imaging, we encounter an enchanting sight on a silver birch twig. The high-resolution image captures xylem vessels alongside phloem cells with astonishing detail—each playing its crucial role in maintaining fluid balance and nutrient transport within this majestic tree. A closer look at water fern rhizome under a light microscope uncovers an interconnected network tissues supporting its underground growth. These structures ensure efficient distribution of resources necessary for survival in challenging environments. Examining pine tree stems through light microscopy allows us to appreciate how intricately woven strands contribute to their robustness and longevity—a testament to nature's engineering marvels. Delving into tomato leaf anatomy via light micrographs reveals densely packed clusters of sieve tube elements forming part of its extensive phloem network—an integral component enabling fruit production and overall plant health. Pondweed stems provide yet another captivating glimpse into the world beneath our feet when observed using advanced microscopic techniques. Phloem fibers intertwine with xylem vessels, showcasing the plant's ability to adapt and thrive in aquatic environments.