Plant Structure Collection (page 3)
"Exploring the Intricate World of Plant Structure: From Chloroplasts to Water Lily Leaves" Delve into the fascinating world of plant structure
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
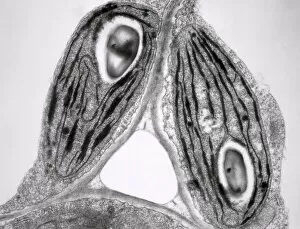
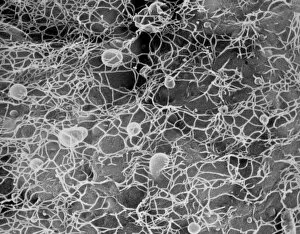
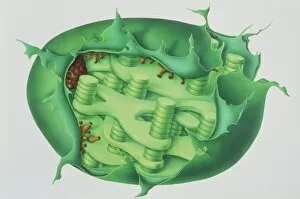
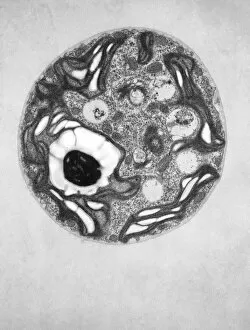
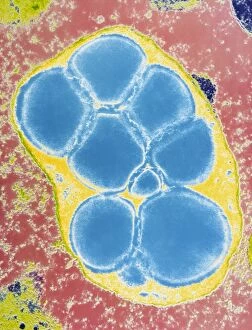
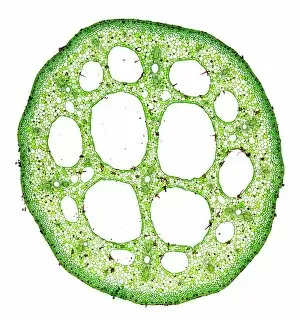
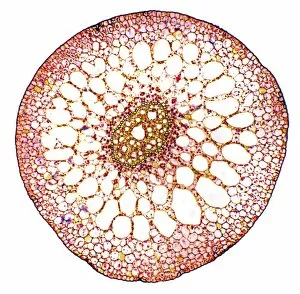
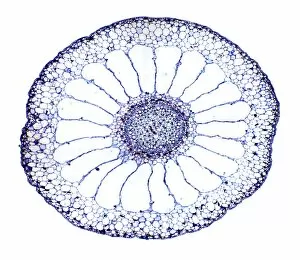
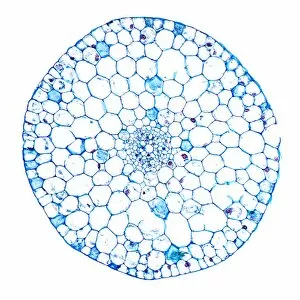
"Exploring the Intricate World of Plant Structure: From Chloroplasts to Water Lily Leaves" Delve into the fascinating world of plant structure, where every cell holds secrets waiting to be unveiled. Take a closer look at the chloroplast in a pea plant cell, a tiny powerhouse responsible for photosynthesis and giving plants their vibrant green hue. Shift your gaze to a mesmerizing light micrograph capturing the intricate details of a water lily leaf. Witness nature's artistry as delicate veins and cells intertwine, creating an exquisite tapestry that allows these aquatic beauties to thrive. Venture further into the microscopic realm with an exploration of various plant cells. Marvel at their diverse shapes and functions, each playing a crucial role in sustaining life on our planet. Amidst this botanical journey, unexpected treasures emerge – like a smoking cap from c. 1880 adorned with embroidered velvet lined with machine-quilted silk. A reminder that even within the study of plants, human creativity finds its place. Turn over pages from sample books dating back to 1890-1895; witness textile patterns blending seamlessly with paper designs. These samples serve as testaments to craftsmanship and innovation throughout history. Discover how even everyday objects like tea caddies carved from wood or side chairs upholstered in beech can reflect elements inspired by nature's own design language. Uncover Berlin woolwork cushion covers from 1850-80, showcasing intricate needlework depicting floral motifs – reminding us that humans have long sought inspiration from plants' beauty and elegance. An oil lamp crafted in 1885 combines brass, glazed earthenware & glass - merging functionality with aesthetics while paying homage to natural forms found within flora itself. As you peruse through more pages filled with pen & ink illustrations combined with textiles on paper sample books (circa 1890-95), immerse yourself deeper into this captivating world where art meets science once again. Rest your feet on a footstool from c.