Hormone Collection (#9)
"Hormone: The Intricate Symphony of the Body's Messengers" The medulla oblongata in the brain, a masterpiece of nature's artwork
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
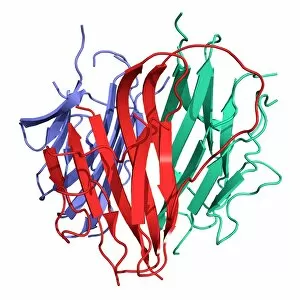
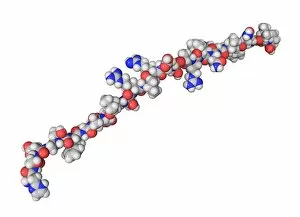
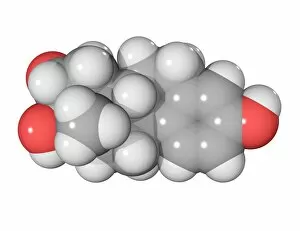
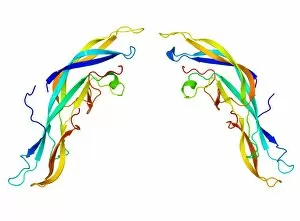
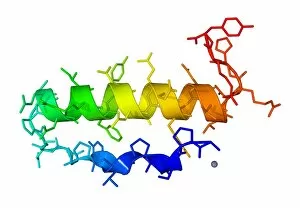
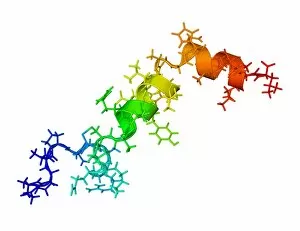
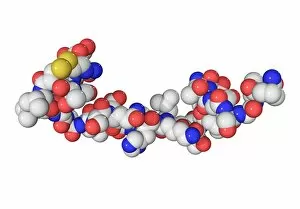
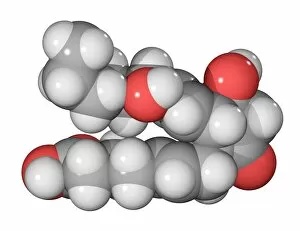
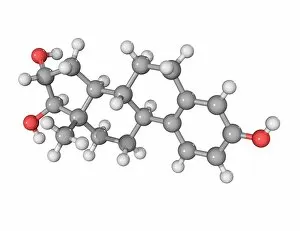
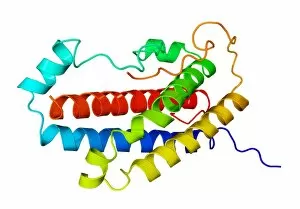
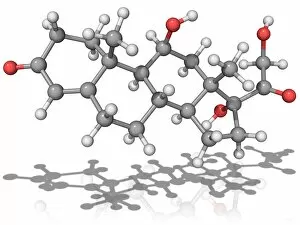
"Hormone: The Intricate Symphony of the Body's Messengers" The medulla oblongata in the brain, a masterpiece of nature's artwork, orchestrates an intricate dance of hormones. Among them, oxytocin hormone crystals shimmer like precious gems under the microscope (PLM C016 / 7196), revealing their profound role in human connection and bonding. Delving deeper into cellular realms, a colored SEM image showcases mitochondria within ovarian cells, highlighting their crucial involvement in hormone production. Meanwhile, light micrographs capture oxytocin crystals (LM C016 / 7195) and insulin crystals (C017 / 8249), unveiling their mesmerizing structures that hold vital functions within our bodies. Exploring athlete physiology through captivating artwork unveils the remarkable impact hormones have on performance and endurance. These chemical messengers drive athletes to push beyond limits and achieve greatness. Artistic depictions also shed light on the complex world of molecular biology. An intricately designed insulin molecule stands as a testament to its pivotal role in regulating blood sugar levels while offering hope for those with diabetes. The pancreas anatomy comes alive through vibrant illustrations showcasing its significance as both an endocrine and digestive organ. It secretes essential hormones such as insulin that keep our bodies functioning optimally. Testosterone takes center stage with PLM capturing crystal formations that symbolize strength and masculinity. This hormone plays a fundamental role not only in physical development but also influences mood, cognition, and overall well-being. Returning to oxytocin - known as the "love hormone" - we delve into its dual identity as both neurotransmitter and hormonal messenger. Its delicate crystalline structure reveals itself once again under microscopic scrutiny (Oxytocin hormone crystals). Lastly, an artistic portrayal of thyroid anatomy reminds us how this small gland holds immense power over metabolism regulation (artwork C013 / 4675). Hormones secreted by this butterfly-shaped organ impact our energy levels, weight management, and overall health.