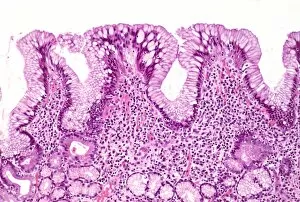
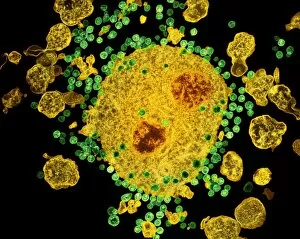
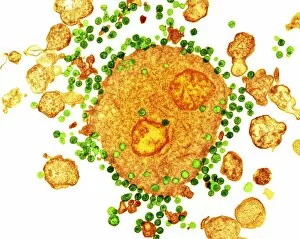
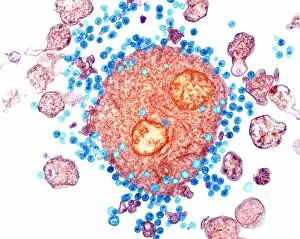
Leukocyte Collection (#4)
"Exploring the Mighty Defenders: Leukocytes and their Battle against Disease" In this captivating collection of images, we delve into the fascinating world of leukocytes
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
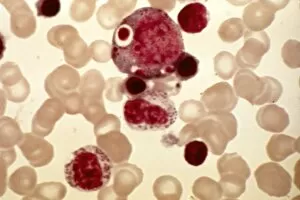
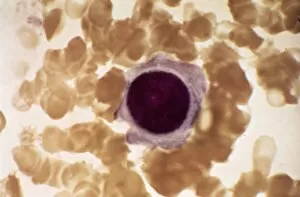
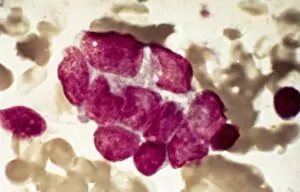
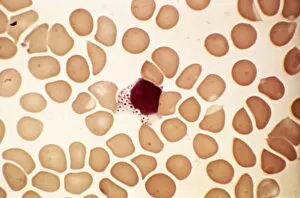
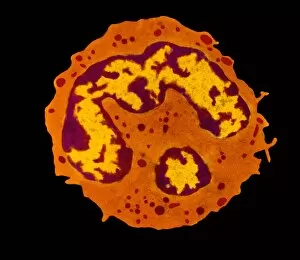
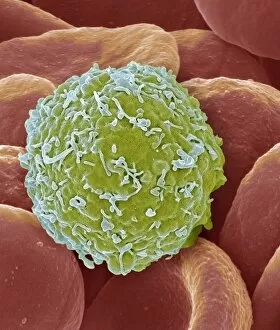
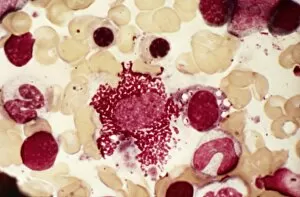
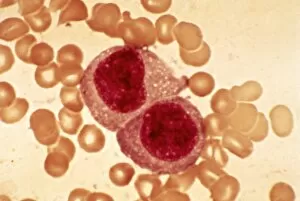
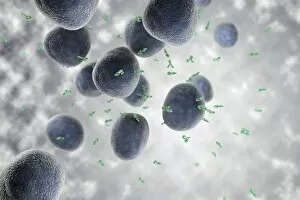
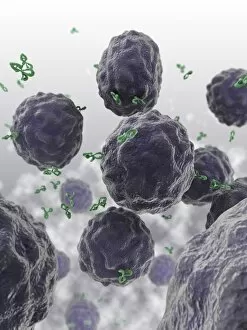
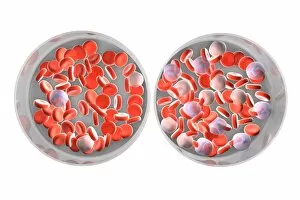
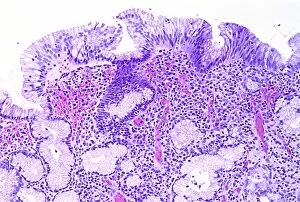
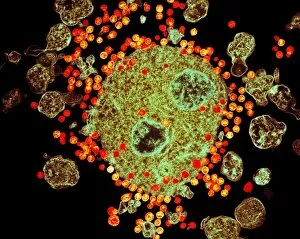
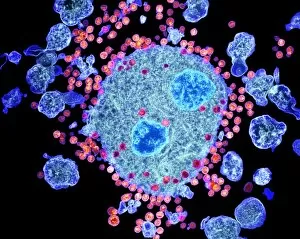
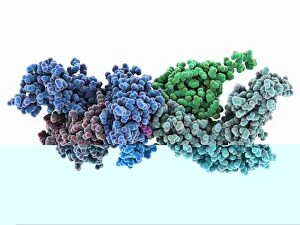
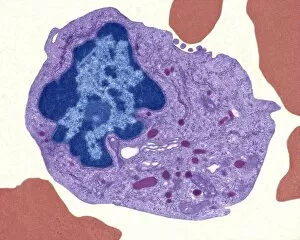
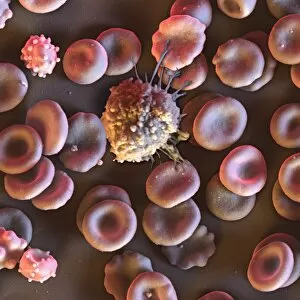
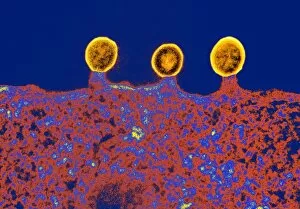
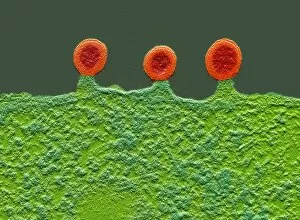
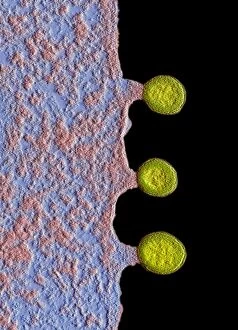
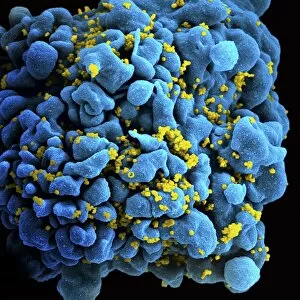
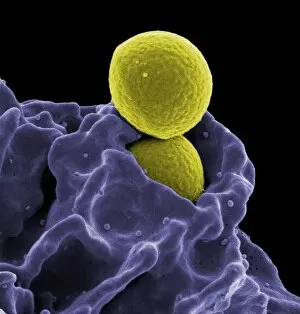
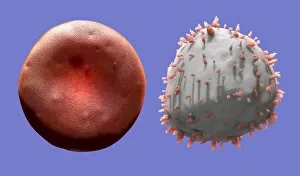
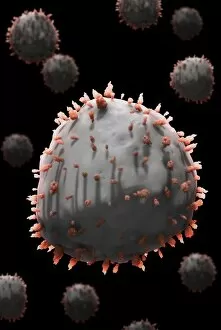
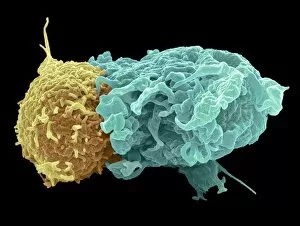
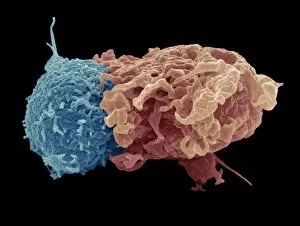
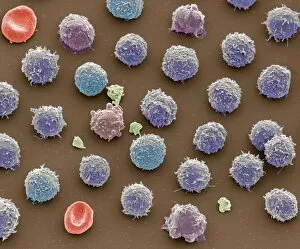
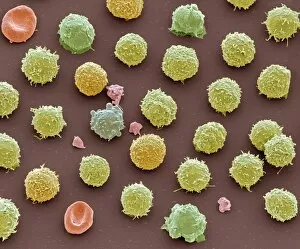
"Exploring the Mighty Defenders: Leukocytes and their Battle against Disease" In this captivating collection of images, we delve into the fascinating world of leukocytes, our body's mighty defenders against various diseases. First up, we witness the incredible power of T lymphocytes as they engage in a fierce battle with cancer cells. SEM C001 / 1679 reveals an epic showdown between these two forces. Moving on to another remarkable image, Neutrophil engulfing MRSA (SEM C018 / 8596) showcases the extraordinary ability of neutrophils to devour harmful bacteria such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Next, TEM unveils a close-up view of a human white blood cell bearing HLA antigen. This intricate image highlights the complexity and diversity within our immune system. A burst of color awaits us in Coloured SEM of a white blood cell (lymphocyte), showcasing the vibrant nature that lies within these essential cells. Meanwhile, Basophil white blood cell reminds us that even amidst chaos, there are specialized warriors ready to combat any threat. The delicate balance between red and white blood cells is beautifully captured in Red and white blood cells (SEM). This harmonious coexistence ensures our bodies remain healthy and functional. Micrograph enthusiasts will appreciate Dohle bodies in blood cell micrograph - an intriguing glimpse into abnormal cellular structures that can indicate certain health conditions like infections or inflammation. Shifting gears towards Plasma cells (TEM), we witness their crucial role in producing antibodies to fight off infections effectively. Their unique appearance underlines their significance in maintaining our overall well-being. Acute promyelocytic leukemia takes center stage next with its distinct features showcased through a powerful micrograph. This visual representation sheds light on this specific type of cancer affecting immature myeloid cells. Phagocytosis takes center stage once again as fungal spores become prey for vigilant macrophages in Phagocytosis of fungal spores (SEM).