Red Blood Cell Collection (#3)
Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, are the most abundant type of blood cell in our bodies
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
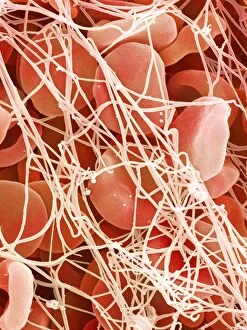
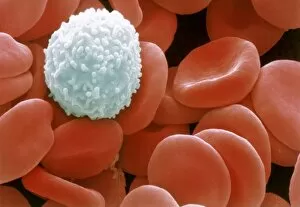
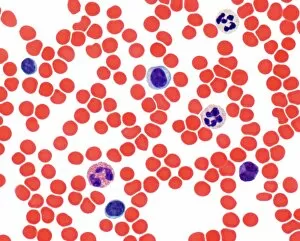
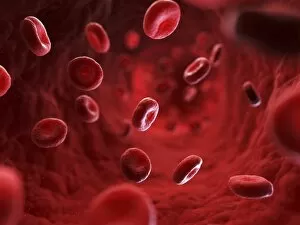
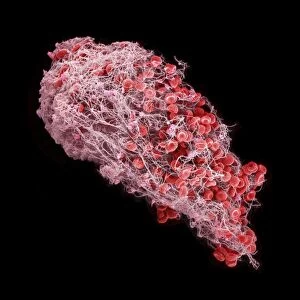
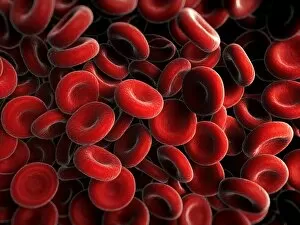
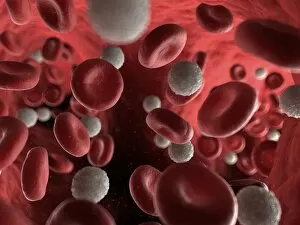
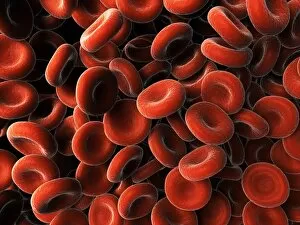
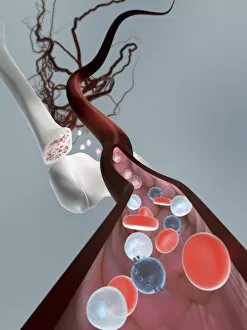
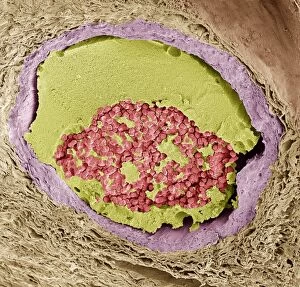
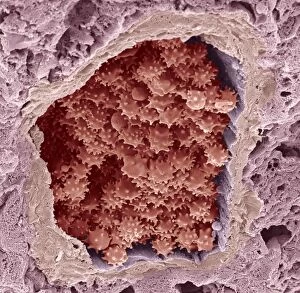
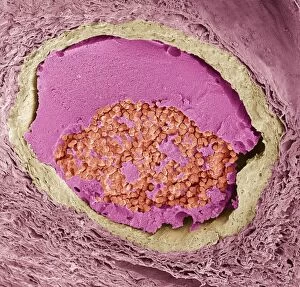
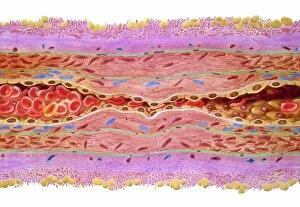
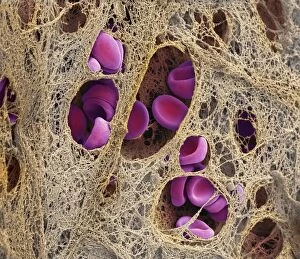
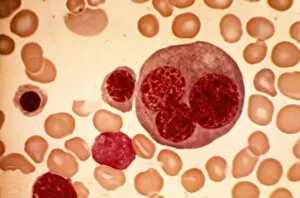
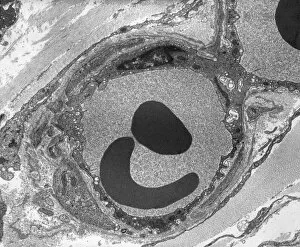
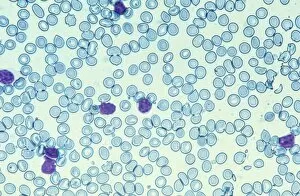
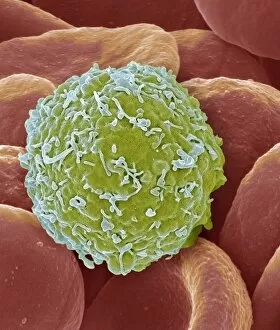
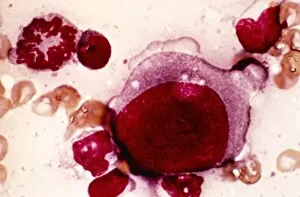
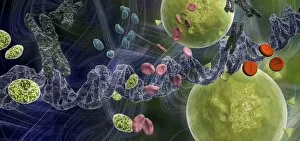
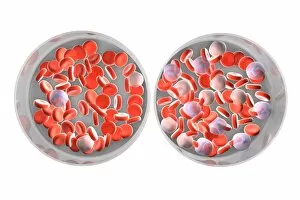
Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, are the most abundant type of blood cell in our bodies. These tiny cells play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. In athlete physiology they can especially important as they carry oxygen from the lungs to every part of the body. This ensures that muscles receive an adequate supply of oxygen during physical activity, enhancing performance and endurance. Artwork depicting the intricate structure of red blood cells showcases their unique shape - biconcave discs without nuclei. This design allows for flexibility and efficient transport through narrow capillaries. The process of blood coagulation cascade is essential for wound healing and preventing excessive bleeding. Artwork illustrating this complex mechanism highlights how red blood cells interact with platelets and clotting factors to form a stable clot, sealing off damaged vessels. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images provide detailed views of various aspects related to red blood cells. One such image displays a close-up view of a blood clot formed by these specialized cells (SEM C016 / 9747). Another SEM image reveals infected red blood cells invaded by mouse malaria parasites (SEM). A diagram showcasing the bloodstream inside a vein demonstrates how red and white blood cells along with platelets flow together within our circulatory system. It emphasizes their collective effort in delivering nutrients, removing waste products, and defending against pathogens. Computer artwork beautifully portrays vibrant red blood cells flowing through arteries and veins, emphasizing their vital role in sustaining life throughout our bodies. Lastly, highlighting the connection between red blood cells and heart reminds us that these remarkable microscopic entities work tirelessly alongside our cardiovascular system to ensure proper circulation throughout every organ and tissue.