Retina Collection (#5)
The retina, a fascinating structure within the human eye, has captivated scientists and artists alike throughout history
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
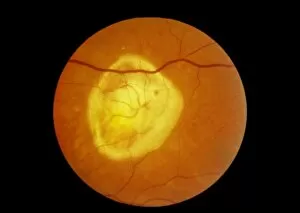
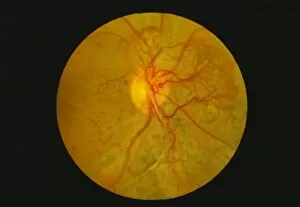
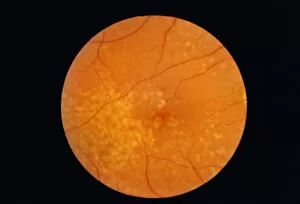
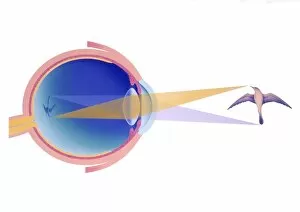
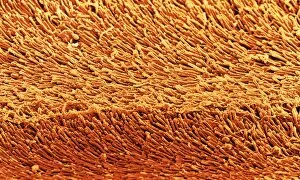
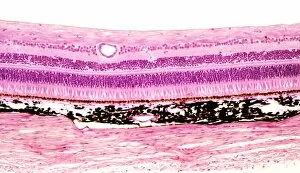
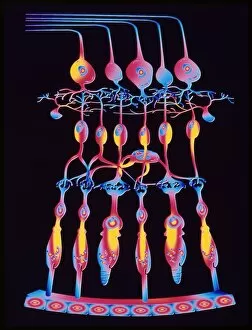
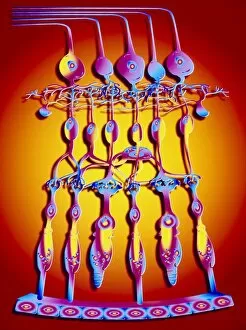
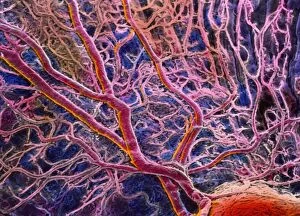
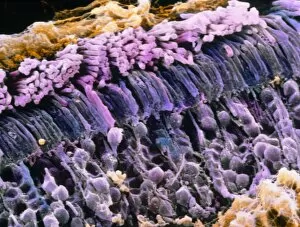
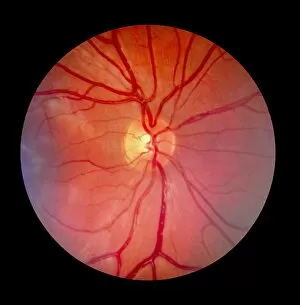
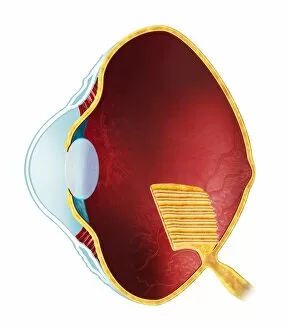
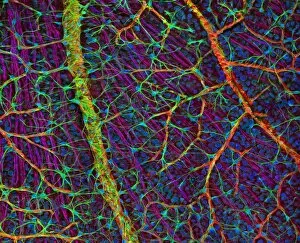
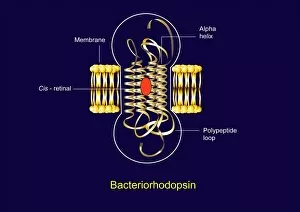
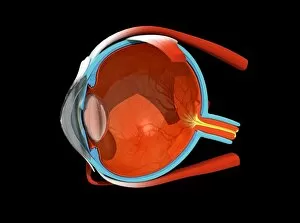
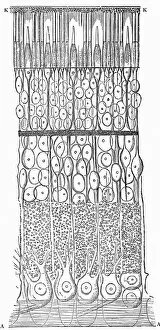
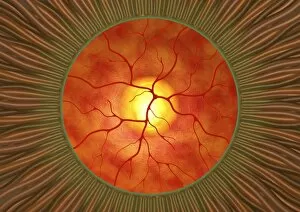
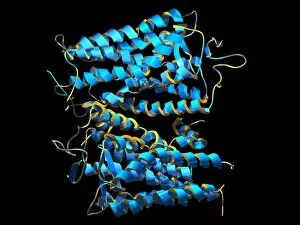
The retina, a fascinating structure within the human eye, has captivated scientists and artists alike throughout history. From histological diagrams to intricate artwork, the intricacies of its anatomy have been meticulously studied and depicted. In the 17th century, Descartes' optics theory shed light on how light interacts with the retina. This groundbreaking understanding paved the way for further exploration into this complex organ. An engraving from 1899 beautifully illustrates the external anatomy of the human eye, showcasing how it works in harmony with the retina. The rod and cone cells of the eye are highlighted in another image taken through a scanning electron microscope (SEM), revealing their delicate structures responsible for vision. Advancements in technology have allowed us to delve deeper into studying retinas through biometric scans. These scans provide valuable insights into individual characteristics and contribute to fields like artificial intelligence. A captivating false-color SEM image showcases a central fovea within a retina—an area crucial for sharp vision—highlighting its intricate details that make it an essential part of our visual system. At a molecular level, rhodopsin protein molecules play a vital role in converting light signals received by retinal cells into electrical impulses sent to our brain—a process critical for sight perception. As we explore further, we discover not only its anatomical features but also its network of blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to sustain this remarkable organ's functionality. From ancient theories to modern scientific discoveries, artful depictions or microscopic examinations—the study of retinas continues to intrigue us as we unravel more about one of nature's most incredible creations: our eyes.