Secondary Structure Collection (page 3)
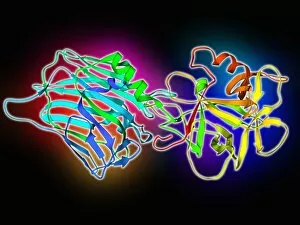
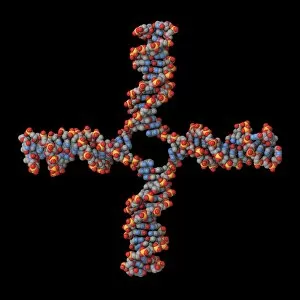
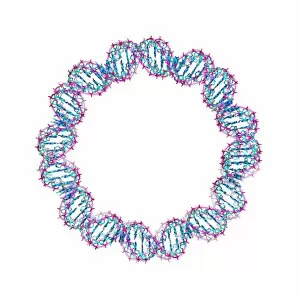
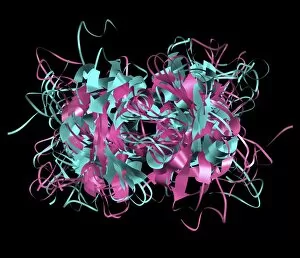
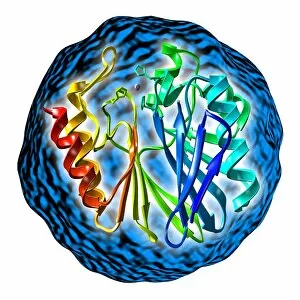
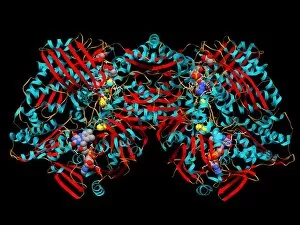
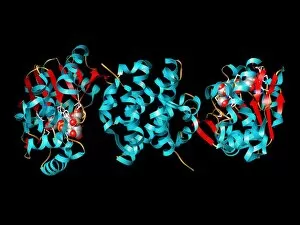
Secondary structure refers to the intricate folding patterns that proteins and nucleic acids adopt, playing a crucial role in their functionality
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
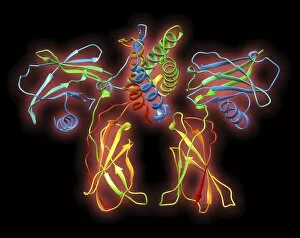
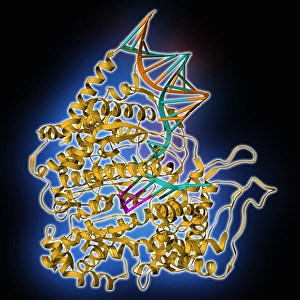
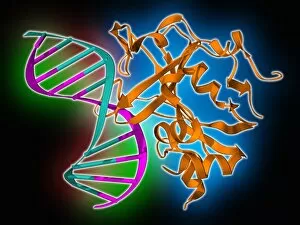
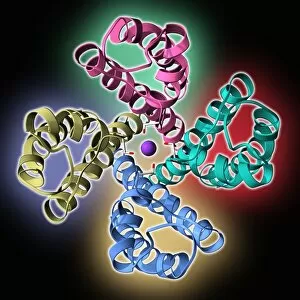
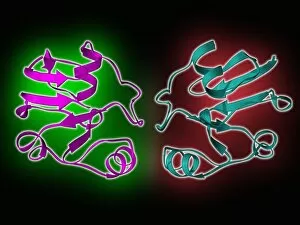
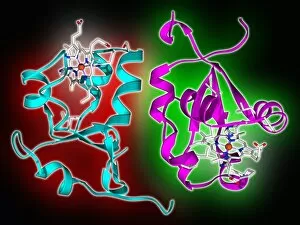
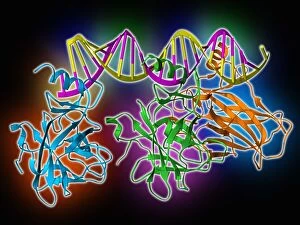
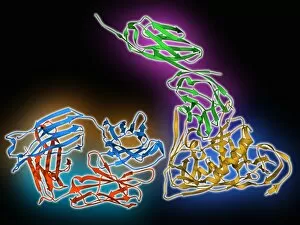
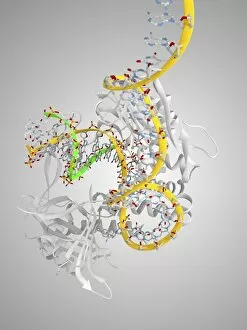
Secondary structure refers to the intricate folding patterns that proteins and nucleic acids adopt, playing a crucial role in their functionality. In one captivating image, an anaesthetic inhibits an ion channel (C015/6718), highlighting how secondary structure impacts cellular processes. Another snapshot showcases DNA transcription, unveiling the molecular model of this essential process. Artwork depicting the secondary structure of proteins captivates our imagination as we marvel at the intricacy and beauty within each fold. The nucleosome molecule further emphasizes this complexity, showcasing how DNA wraps around histone proteins to form a compact structure. The bacterial ribosome stands tall as a testament to secondary structures' significance in protein synthesis. Meanwhile, the HIV reverse transcription enzyme reminds us of its vital role in converting viral RNA into DNA during infection. Molecular models provide insight into hepatitis C virus enzymes and interferon molecules—both critical players in disease progression and immune response modulation. Similarly, human growth hormone molecules hold immense importance for development and metabolism regulation. Exploring coagulation factor complex molecules (C014/0139) unravels mechanisms behind blood clotting—a process dependent on precise secondary structures working together seamlessly. Ghrelin hormone molecules intrigue us with their involvement in appetite regulation and energy balance maintenance. From anaesthetics influencing ion channels to hormones orchestrating bodily functions, understanding secondary structures unlocks countless mysteries within biological systems. These captivating images remind us of the intricate dance occurring at a microscopic level—the delicate folds dictating life's grand symphony.