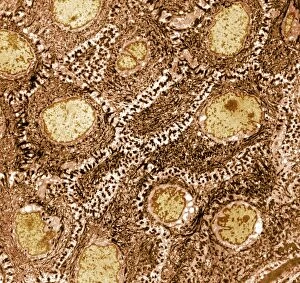
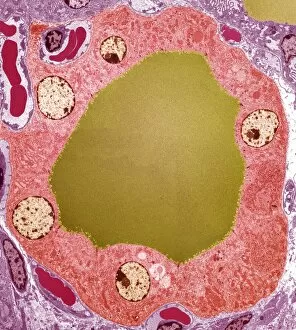
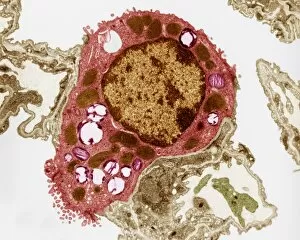
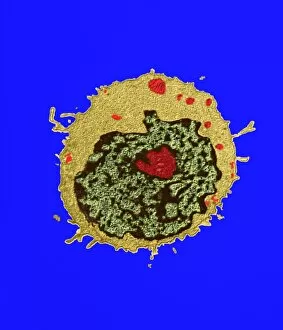
Transmission Electron Micrograph Collection (#7)
"Exploring the Microscopic World: Unveiling Intricate Structures through Transmission Electron Micrograph" In the realm of science
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
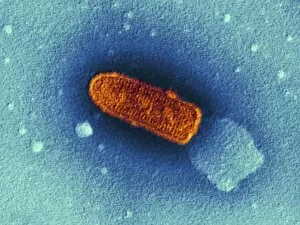
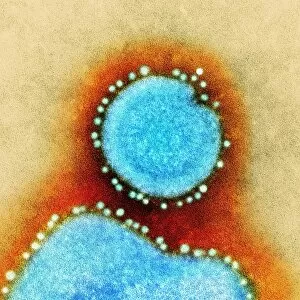
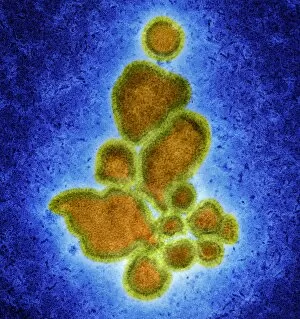
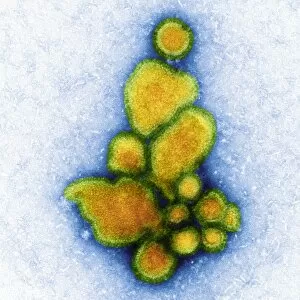
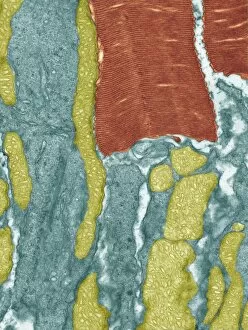
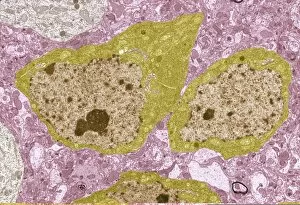
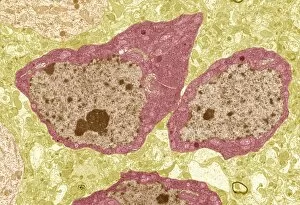
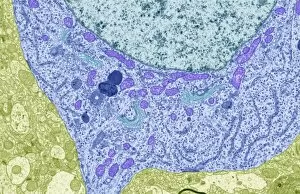
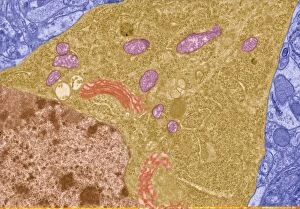
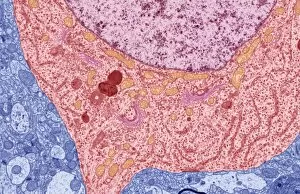
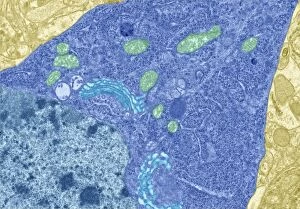
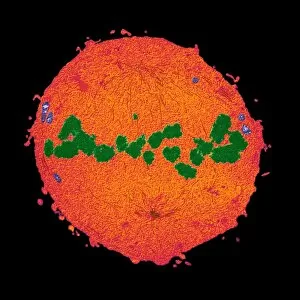
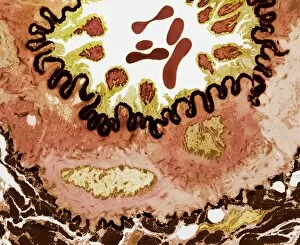
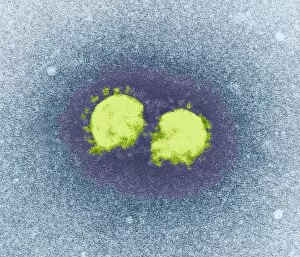
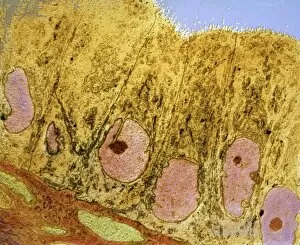
"Exploring the Microscopic World: Unveiling Intricate Structures through Transmission Electron Micrograph" In the realm of science, transmission electron micrographs (TEM) have revolutionized our understanding of various biological entities. These powerful images provide a glimpse into the hidden intricacies that make up our world at an unimaginably small scale. One captivating TEM showcases regenerating nerve cells, offering hope for those seeking to understand and treat neurological disorders. The image captures the delicate process of nerve cell regrowth, highlighting their remarkable ability to heal and restore function. Another fascinating TEM reveals fat cells in all their glory - spherical structures filled with lipid droplets that play crucial roles in energy storage and insulation within our bodies. This microscopic view sheds light on how these adipocytes contribute to overall health and metabolism. Moving on, we encounter an E. coli bacterium captured by TEM, showcasing its distinctive rod-shaped structure. This notorious bacterium serves as both a model organism for research purposes and a cause of concern due to its potential pathogenicity. Delving deeper into the microscopic world, plasma cells come into focus through another mesmerizing TEM image. These specialized white blood cells produce antibodies vital for immune defense against invading pathogens - a testament to the intricate mechanisms at work within our bodies. The hauntingly beautiful transmission electron micrograph of influenza virus particles provides insight into one of humanity's greatest challenges - infectious diseases. Studying such images aids scientists in developing effective vaccines and antiviral treatments against these elusive viral foes. Hepatitis C viruses also reveal themselves under TEM scrutiny, reminding us of the ongoing battle against this chronic liver disease affecting millions worldwide. Understanding their structure helps researchers devise strategies for prevention and treatment. Shifting gears slightly from infections to anatomy, an eye muscle is showcased through TEM imagery – revealing its unique fiber arrangement responsible for precise eye movements essential for vision coordination. A Purkinje nerve cell takes center stage next; this neuron found in the cerebellum plays a crucial role in coordinating movement and balance.