Xylem Collection (#2)
Xylem, the intricate network of plant tissues responsible for water transport and structural support, is a fascinating subject to explore under various microscopes
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
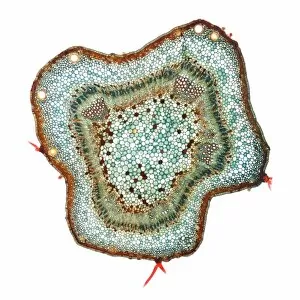
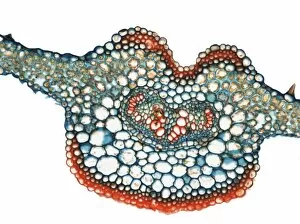
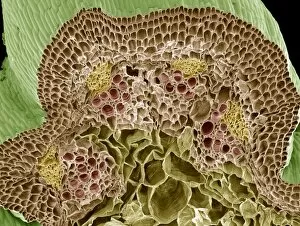
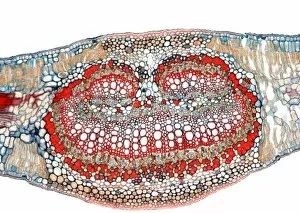
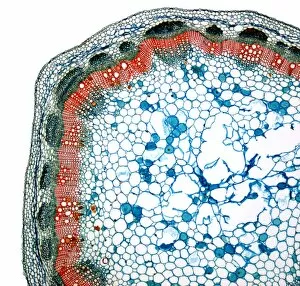
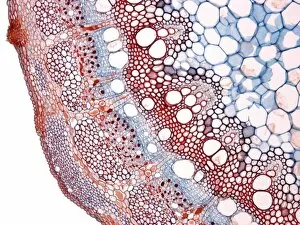
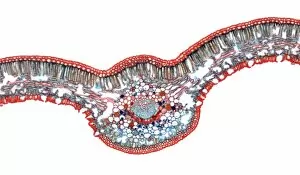
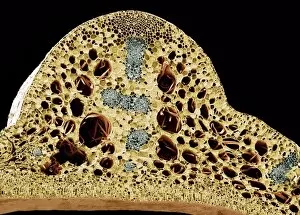
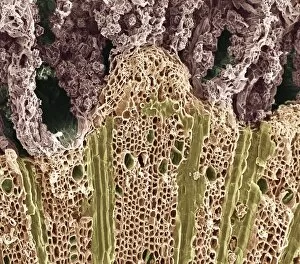
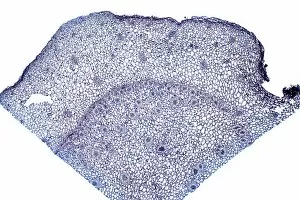
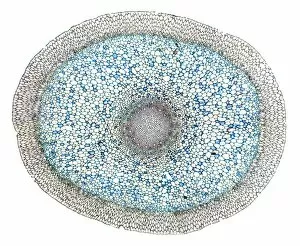
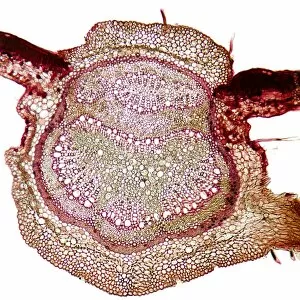
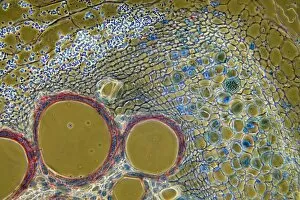
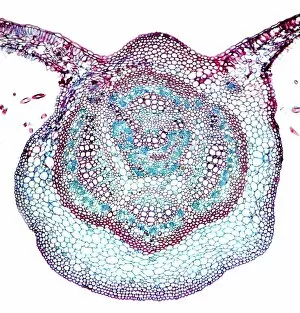
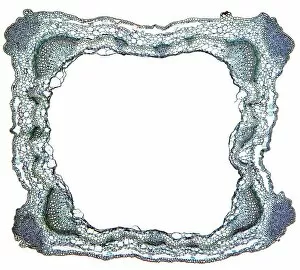
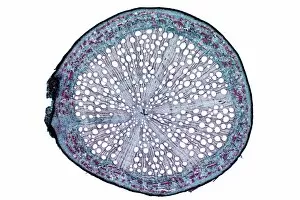
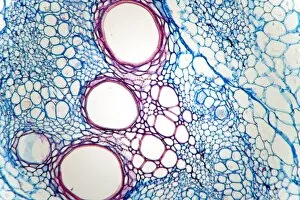
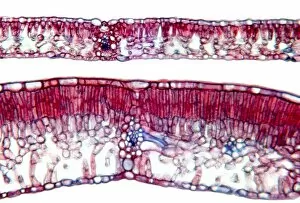
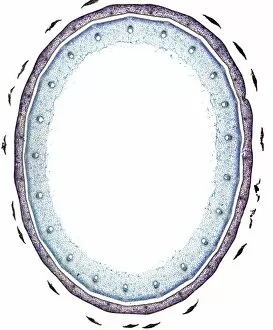
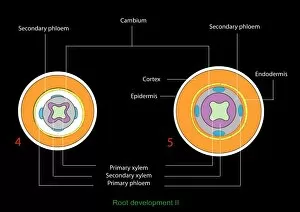
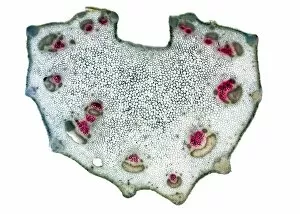
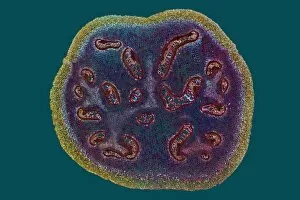
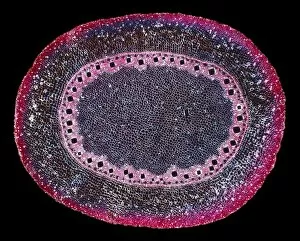
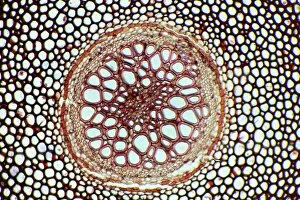
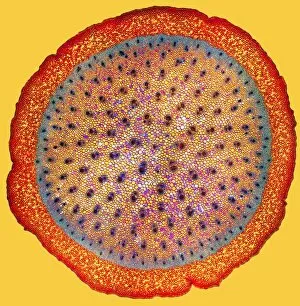
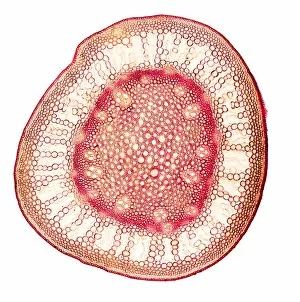
Xylem, the intricate network of plant tissues responsible for water transport and structural support, is a fascinating subject to explore under various microscopes. From scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images capturing the detailed vascular bundles to light micrographs showcasing different plant parts, xylem reveals its beauty and functionality. In a castor oil stem captured by a light micrograph, we witness the complexity tissue as it forms an interconnected system of vessels that efficiently transports water from roots to leaves. Similarly, in a maize root image taken with a light microscope, we can observe the organized arrangement cells that enable efficient uptake of water and nutrients. Moving on to leaf structures, a captivating light micrograph showcases the delicate veins within a water lily leaf. These intricate networks are composed mainly tissue which ensures proper hydration throughout the leaf's surface area. Another stunning SEM image captures silver birch twig's xylem vessels in detail - their elongated shapes perfectly adapted for fluid transportation. Exploring further into plants' underground systems, we encounter an enchanting light micrograph displaying the rhizome structure of a water fern. Xylem tissues play an essential role here too by providing support and facilitating nutrient absorption from surrounding soil particles. Light micrographs also capture xylem wonders in stems like those found in pine trees or pondweeds. Pine tree stems exhibit dense clusters of tracheids – specialized cells within xylem – while pondweed stems showcase long strands forming hollow tubes for efficient water movement. Even at smaller scales observed through SEM imaging techniques, such as examining isolated samples of pure xylem tissue or wood itself under high magnification power; one can appreciate its intricate cellular arrangements that allow for optimal fluid flow and mechanical stability. Lastly, exploring below ground once again brings us to oak roots depicted through another mesmerizing light micrograph.