Cuticle Collection
"Exploring the Intricate World of Cuticles: From Water Lily Leaves to Giant Panda Hair" Delicate and ethereal
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
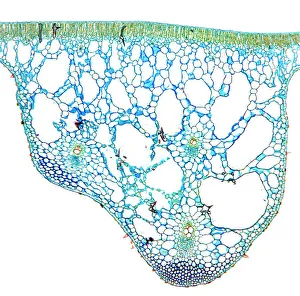
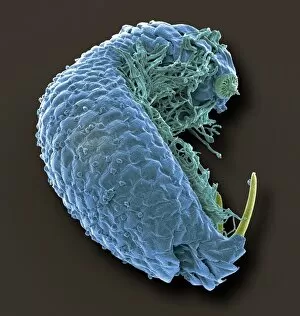
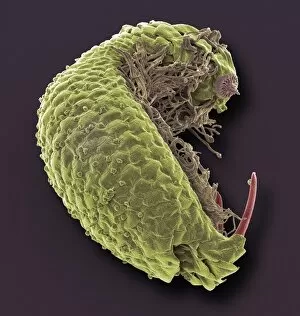
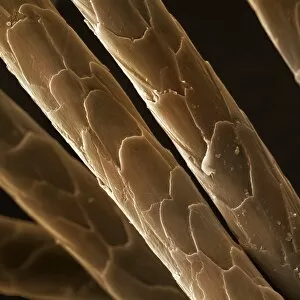
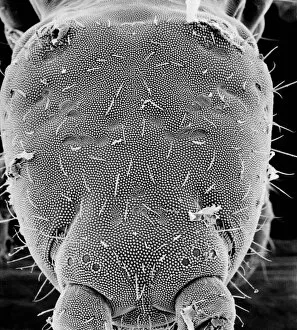
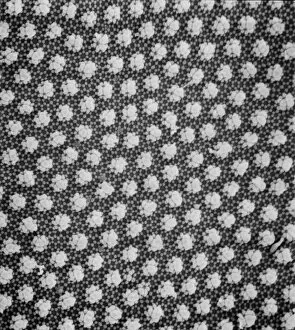
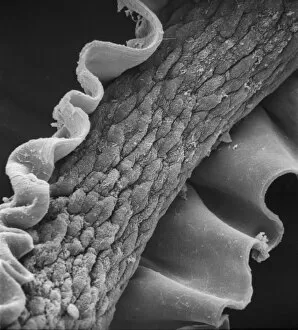
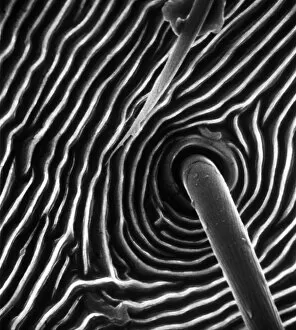
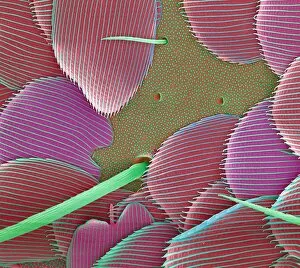
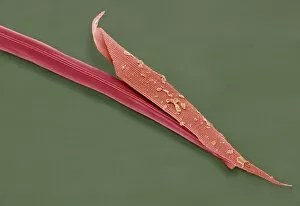
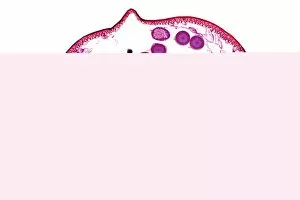
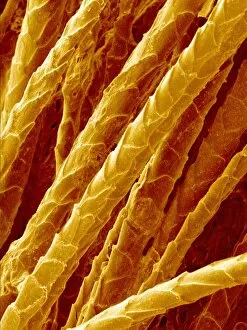
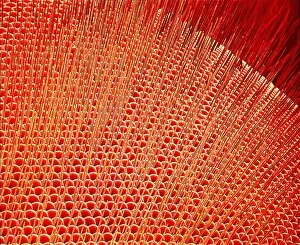
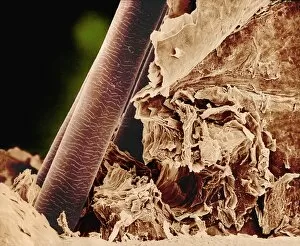
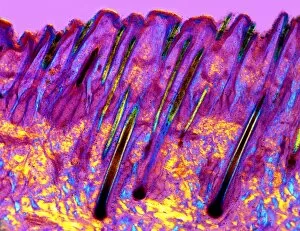
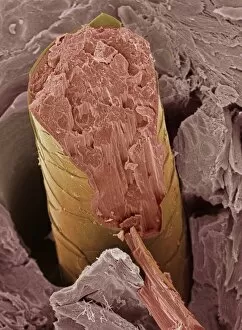
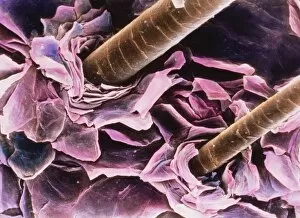
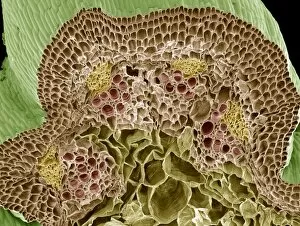
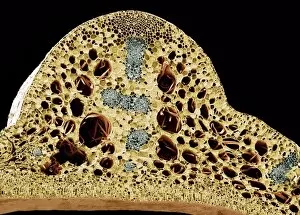
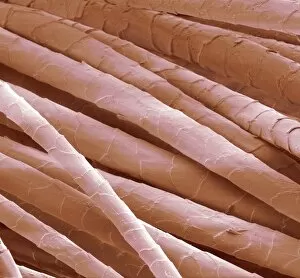
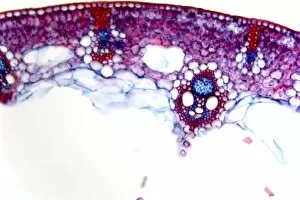
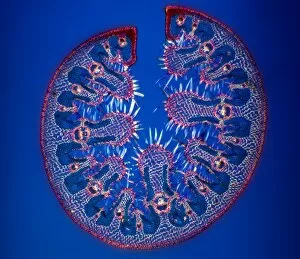
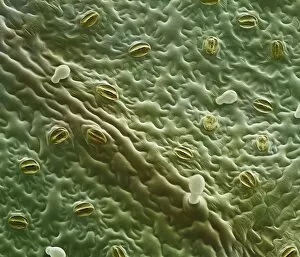
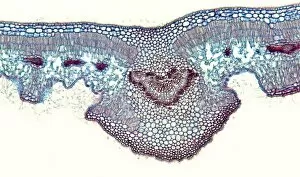
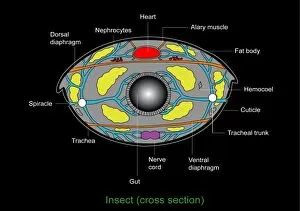
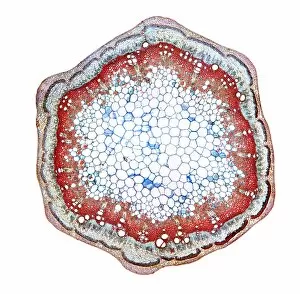
"Exploring the Intricate World of Cuticles: From Water Lily Leaves to Giant Panda Hair" Delicate and ethereal, the water lily leaf showcases its intricate cuticle structure under a light micrograph. Unveiling the evolution of beauty culture, a vintage black and white photo captures the electric manicure machine revolutionizing nail care. Nature's artistry at play: glistening water droplets delicately rest on a leaf's cuticle, creating an enchanting sight. Peering into the microscopic world, a biomedical illustration reveals the complex anatomy of a roundworm's cuticle – nature's armor for survival. Human hair takes center stage as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) unravels its fascinating structural details with astonishing clarity. Not just limited to humans, SEM delves into dog hair too, unraveling its unique composition and texture in mesmerizing detail. A captivating SEM image showcases giant panda hair in all its glory – each strand revealing nature's mastery in providing insulation and protection. Gastrotrichs take their turn under SEM scrutiny, showcasing their intriguing cuticular features that aid them in aquatic habitats. Another glimpse into human hair through SEM highlights its diverse textures and patterns – truly reflecting individuality at its finest. In this captivating journey through various specimens captured by cutting-edge technology like SEM or traditional photography methods like light micrographs, we discover how different organisms possess unique yet equally fascinating cuticles - from delicate leaves to human hairs or even gastrotrichs thriving underwater. The intricacies hidden within these seemingly ordinary structures remind us of nature’s remarkable ability to adapt and protect living beings across species boundaries.