Pathogenic Collection (page 6)
Pathogenic microorganisms are microscopic entities that pose a significant threat to human health
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
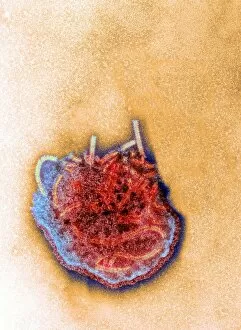
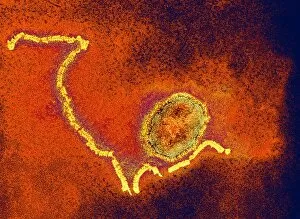
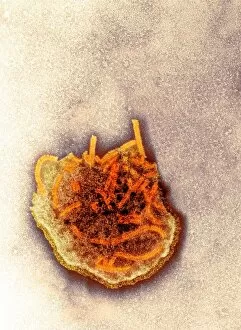
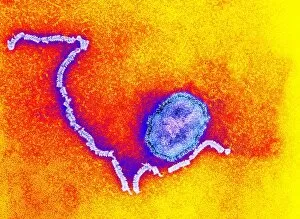
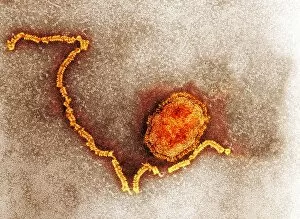
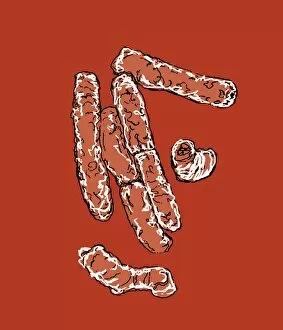
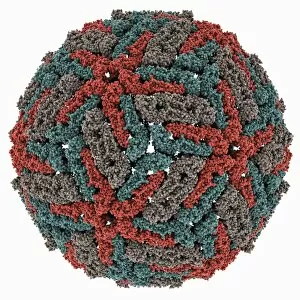
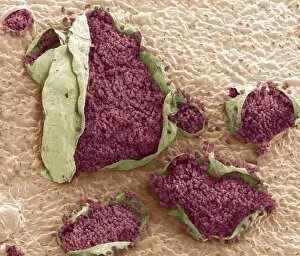
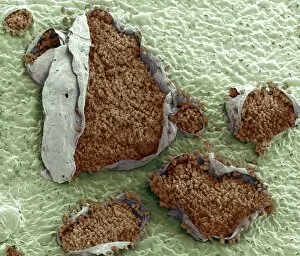
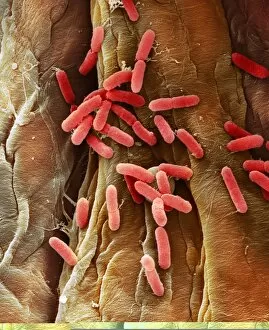
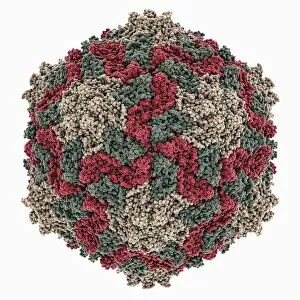
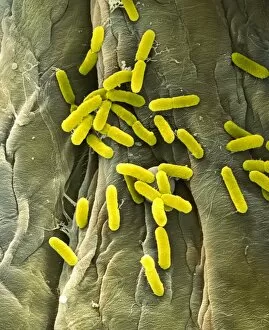
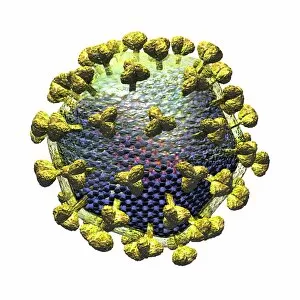
Pathogenic microorganisms are microscopic entities that pose a significant threat to human health. From budding yeast cells to avian flu viruses, these tiny organisms have the potential to cause widespread diseases and infections. In the world of pathogens, the avian flu virus stands out as one of the most notorious culprits. Its ability to jump from birds to humans has sparked global concerns about pandemics and led scientists on a quest for effective prevention strategies. Neutrophils, our body's first line of defense against infection, play a crucial role in engulfing harmful bacteria like MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). This SEM image captures this incredible process, showcasing how neutrophils work tirelessly to protect us from pathogenic invaders. Salmonella bacteria are another well-known pathogen responsible for causing foodborne illnesses worldwide. This SEM image provides an up-close look at their unique structure and highlights their capacity for survival in various environments. The HIV particle is infamous for its devastating impact on the immune system. Understanding its intricate structure has been instrumental in developing antiretroviral therapies that help manage this deadly virus. Anthrax cultures depicted in historical diagrams remind us of past outbreaks and highlight the importance of ongoing research into preventing bioterrorism threats associated with this highly infectious disease. Norovirus particles captured through TEM imaging reveal their distinctive shape and shed light on why they are so contagious. Responsible for many cases of gastroenteritis, noroviruses can spread rapidly within communities if proper hygiene measures aren't followed diligently. Tuberculosis bacteria continue to be a major global health concern due to their ability to infect millions each year. Efforts towards improved diagnostics and treatment options remain critical in combating this persistent pathogen. E. coli bacteria serve as both harmless inhabitants of our gut flora but also dangerous pathogens when certain strains acquire virulence factors. This diverse bacterium reminds us that not all E. coli strains are created equal.