Supportive Collection (#3)
"Supportive: Exploring the Intricate World of Nature's Structures" Delving into the microscopic realm
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
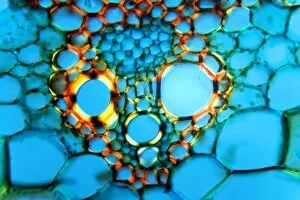
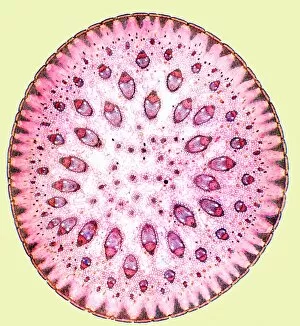
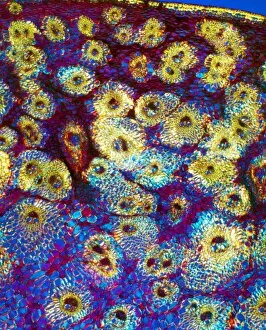
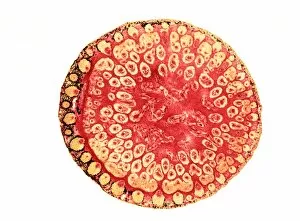
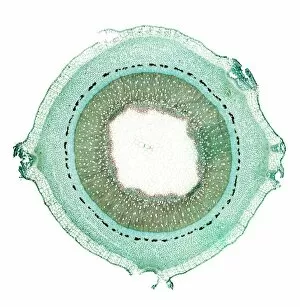
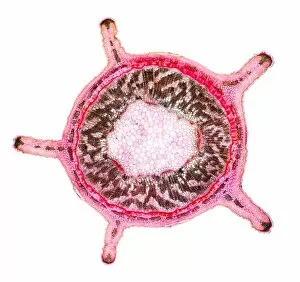
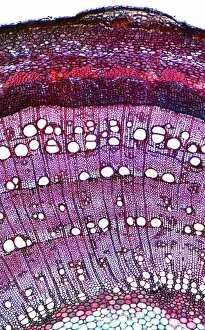
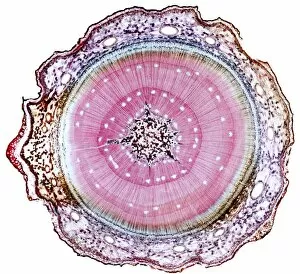
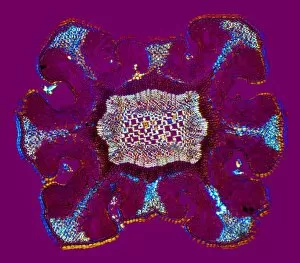
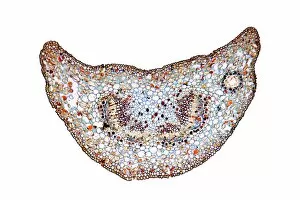
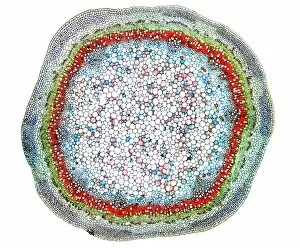
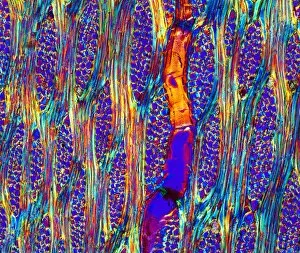
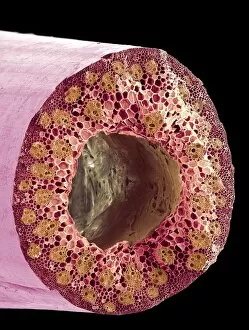
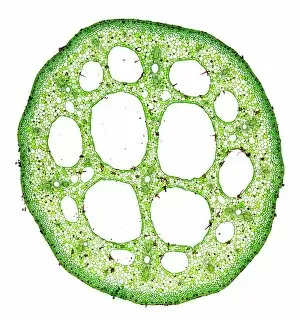
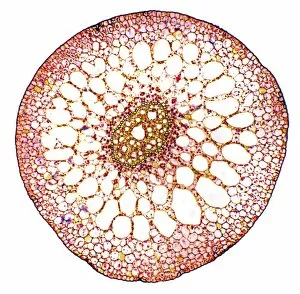
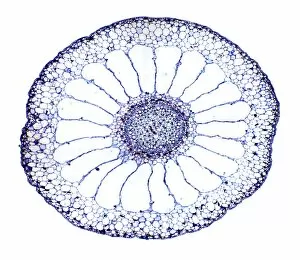
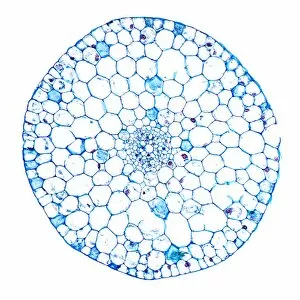
"Supportive: Exploring the Intricate World of Nature's Structures" Delving into the microscopic realm, a diatom reveals its intricate beauty under the scanning electron microscope (SEM). Its delicate structure serves as a reminder of nature's supportive designs. The water lily leaf, captured in a mesmerizing light micrograph, showcases the resilience and strength found in nature. Its ability to support itself amidst turbulent waters is truly remarkable. Venice's iconic buildings stand tall on their foundations, an artwork known as C016 / 7703. These sturdy structures symbolize the importance of strong support systems in our lives. Astrocyte nerve cells, with their elaborate branching patterns and interconnectedness, demonstrate how vital it is to have supportive networks within our own minds and bodies. Xylem tissue, magnified through SEM imaging, exemplifies nature's ingenious way of transporting water and nutrients throughout plants' vascular systems – an essential support mechanism for growth and survival. Wood fibers come alive under the light microscope, displaying their interlocking arrangement that provides stability and durability to trees – a testament to nature's unwavering support for life on Earth. Returning to astrocyte nerve cells once more highlights their significance in supporting brain function by maintaining chemical balance and providing structural support for neurons. Another stunning diatom captures our attention under SEM imaging; its intricate shell-like structure reminds us that even tiny organisms can possess incredible strength when supported by natural design. Revisiting astrocyte nerve cells yet again emphasizes their crucial role in supporting neuronal health through various functions like regulating blood flow or removing toxins from surrounding tissues. Concluding this exploration with another captivating diatom image reminds us of the vast diversity found within these microscopic organisms - each one uniquely adapted with supportive features allowing them to thrive underwater.