Transmission Electron Collection (#6)
"Unlocking the Intricacies of Life
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
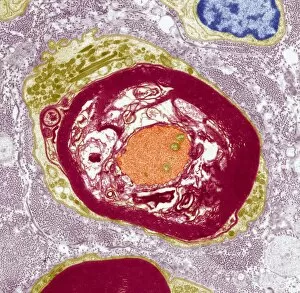
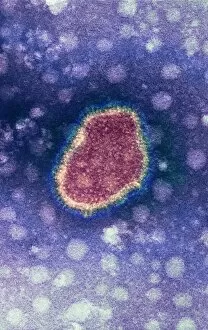
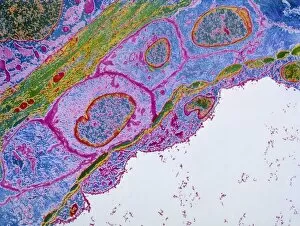
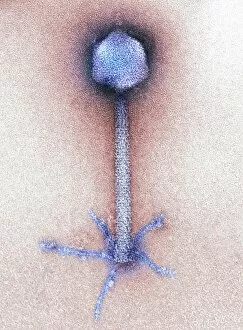
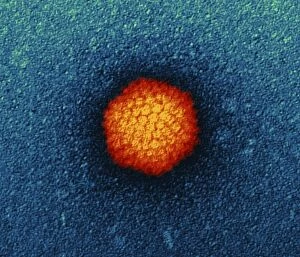
"Unlocking the Intricacies of Life: Exploring the Microscopic World through Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)" Delving into the depths of cellular structures and biological processes, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) has revolutionized our understanding of various aspects of life. With its high-resolution imaging capabilities, TEM allows us to witness intricate details that were once hidden from our sight. At synapse nerve junctions, TEM reveals a mesmerizing dance between neurotransmitters, enabling communication between neurons with remarkable precision. Norovirus particles come alive under TEM's lens, showcasing their unique shape and arrangement – a crucial insight in combating these notorious pathogens. E. Coli bacteria appear as tiny rods when observed through TEM, reminding us of their omnipresence in nature and sometimes unfortunate encounters in human health. Fat cells take on an unexpected beauty when magnified by TEM; their delicate structure resembling a web-like network that stores energy for our bodies. The myelination process is brought to life through TEM images capturing nerve fibers coated with protective sheaths. These stunning visuals help unravel the mysteries behind efficient neural signaling and hold promise for treating demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis. TEM exposes the menacing presence of MRSA-resistant Staphylococcus bacteria – formidable adversaries in healthcare settings worldwide. Another glimpse at E. coli bacterium showcases its intricate internal machinery responsible for vital functions within this single-celled organism. Nerve cells reveal their complexity under TEM's scrutiny – branching dendrites reaching out like tree branches while axons transmit electrical signals across vast distances. Mitochondria steal the spotlight as they power these nerve cells' activities, appearing as dynamic organelles teeming with energy-producing potential. Plasma cells burst forth with vibrant colors when examined using TEM; their role in producing antibodies becomes even more awe-inspiring upon closer inspection. Once again, myelinated nerve fibers captivate us with their elegant architecture – a testament to nature's ingenuity in optimizing neural communication.