Cytological Collection (#8)
"Cytological Wonders Unveiled: Exploring the Intricacies of Cellular Life" In this captivating journey into the microscopic world, we delve into the realm of cytology
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
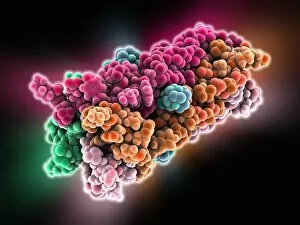
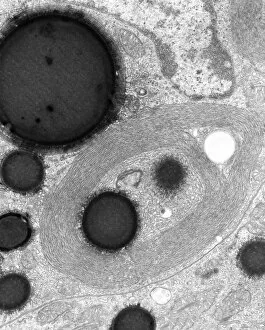
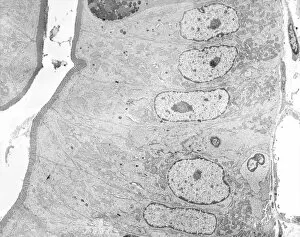
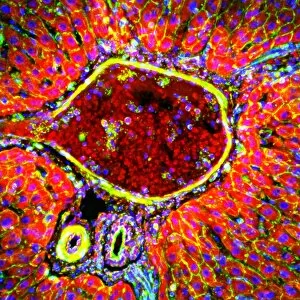
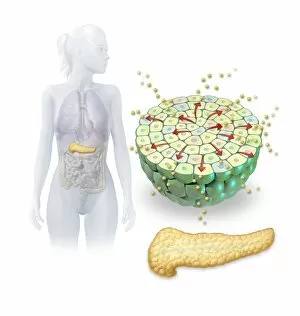
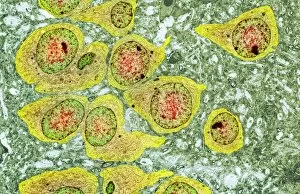
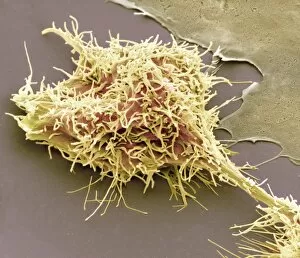
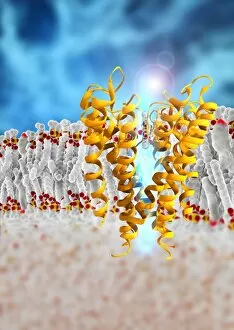
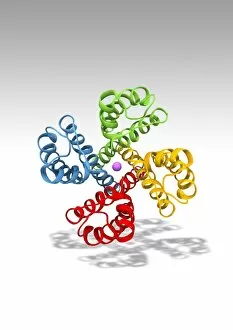
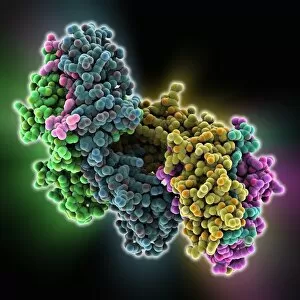
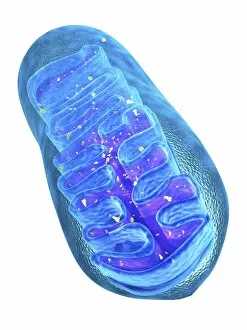
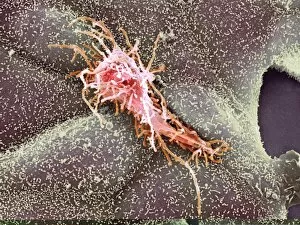
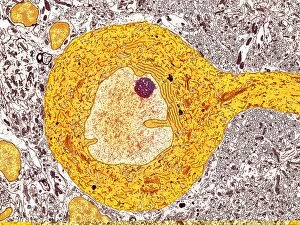
"Cytological Wonders Unveiled: Exploring the Intricacies of Cellular Life" In this captivating journey into the microscopic world, we delve into the realm of cytology, where astonishing discoveries await. From anaesthetic inhibiting an ion channel to mesmerizing light and electron micrographs, each image offers a glimpse into the intricate workings of cells. Firstly, we witness an extraordinary phenomenon as anaesthetic molecules inhibit an ion channel within cells. This interaction sheds light on how these substances affect cellular processes and highlights their potential therapeutic applications. Moving forward, our attention is drawn to HeLa cells captured under a light microscope. The vivid details reveal their complex structures and provide valuable insights for research in various fields such as cancer biology and drug development. Next up is a stunning transmission electron micrograph showcasing the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Its labyrinthine network serves as a hub for protein synthesis and transport within cells, emphasizing its crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. As we shift gears towards artistic representation, dendritic cells take center stage through exquisite artwork. These specialized immune cells play a pivotal role in recognizing foreign invaders and orchestrating immune responses - truly nature's defenders at work. Returning to HeLa cells under another light microscope lens unveils yet another breathtaking display of cellular beauty. Each cell appears like a universe unto itself with intricate organelles working harmoniously to sustain life's delicate balance. The enchantment continues with captivating images capturing mitosis - the process by which one cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Witnessing this dance of chromosomes during cell division provides profound insights into growth, development, and regeneration mechanisms within organisms. Shifting focus from animal to plant life brings us pine pollen grains delicately observed under a light microscope. These tiny particles hold immense significance in plant reproduction dynamics while exhibiting remarkable structural intricacies that aid successful pollination. Further exploring plants' hidden wonders takes us on an enlightening journey through light micrographs of pine and lime tree stems.