Beta Sheet Collection (#8)
The beta sheet, a crucial element in the world of molecular biology and protein structure, plays a significant role in various biological processes
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
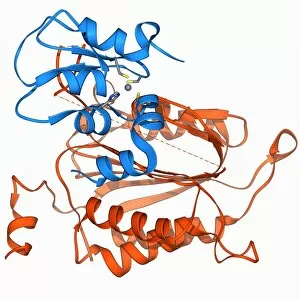
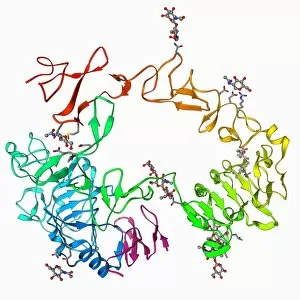
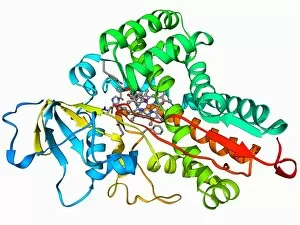
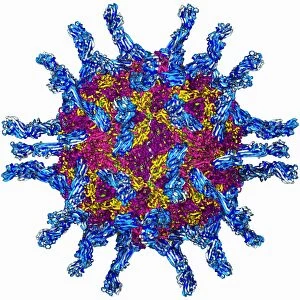
The beta sheet, a crucial element in the world of molecular biology and protein structure, plays a significant role in various biological processes. From DNA transcription to HIV reverse transcription enzyme, this secondary structure of proteins is an intricate masterpiece. In the realm of DNA transcription, the beta sheet takes center stage as it assists in unraveling genetic information. Its molecular model showcases its complexity and elegance, resembling an artistic creation that captivates scientists worldwide. Not only does the beta sheet contribute to DNA transcription, but it also plays a vital role in combating diseases. The Hepatitis C virus enzyme's molecular model reveals how this secondary structure aids in understanding and potentially treating this infectious disease. Another remarkable example lies within Manganese superoxide dismutase enzyme F006 / 9423. This intricate arrangement highlights how the beta sheet contributes to antioxidant defense mechanisms within our bodies. Moreover, Argonaute protein molecule F006 / 9526 demonstrates how the beta sheet collaborates with microRNA to regulate gene expression. This interaction holds immense potential for therapeutic interventions targeting various diseases. Immunoglobulin G antibody and egg white F006 / 9682 showcase yet another fascinating aspect of the beta sheet's versatility. Here we witness its involvement in immune responses against foreign substances present within our bodies. Furthermore, Cytochrome P450 complex F006 / 9669 illustrates how this secondary structure enables drug metabolism and detoxification processes essential for maintaining human health. Succinyl-CoA synthetase enzyme F006 / 9592 emphasizes another critical function of the beta sheet: energy production through cellular respiration pathways. Its presence ensures efficient conversion of succinyl-CoA into ATP molecules necessary for sustaining life processes. Additionally, RNA-induced silencing complex F006 / 9586 unveils how the beta sheet participates in gene regulation by suppressing specific mRNA molecules through small interfering RNAs (siRNAs).